Volume 14, Number 2—February 2008
Research
Genetic Determinants of Virulence in Pathogenic Lineage 2 West Nile Virus Strains
Figure 2
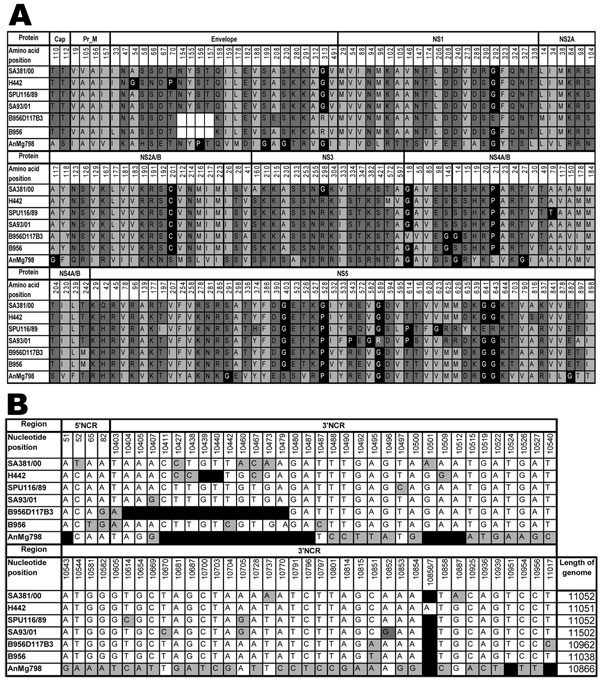
Figure 2. A) Amino acid differences between South African lineage 2 strains of West Nile virus (WNV) strains sequenced in the present study and previously published lineage 2 strains. Strain SA381/00 is less neuroinvasive than the highly neuroinvasive strains SA93/01, H442, and SPU116/89. Light gray, hydrophobic amino acids; dark gray, hydrophilic amino acids; black, structural-determining amino acids; white blocks, deletion of the glycosylation site in the envelope protein of the B956D117B3 strain. Numbering is according to the SA381/00 genome position for specific genes. Cap, capsid; prM, premembrane; NS, nonstructural. B) Nucleotide differences in the noncoding 5′ and 3′ regions of lineage 2 strains. Numbering is according to WNV strain SA381/00. Black, deletions; gray, nucleotide differences. The length of each genome is given in the last column. (Strain AnMg798 is incomplete in the GenBank database and may thus be longer than indicated.)