Volume 17, Number 5—May 2011
Letter
Anaplasma phagocytophilum Infection in Ticks, China–Russia Border
Figure A1
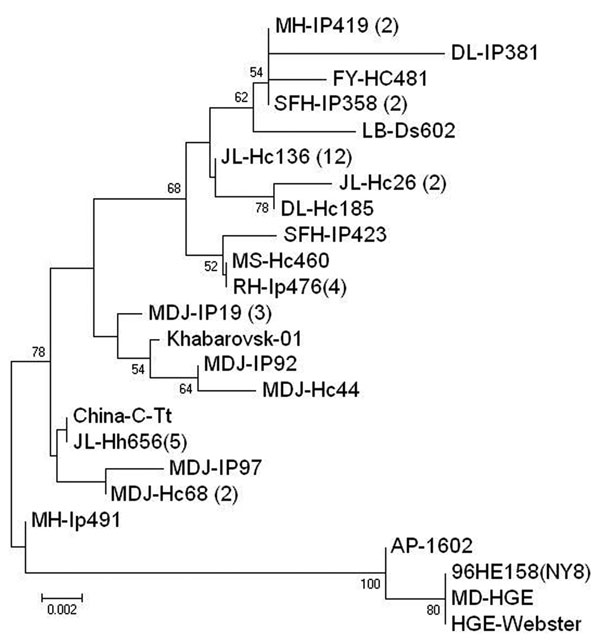
Figure A1. Phylogenetic tree of Anaplasma phagocytophilum based on 348-bp the citrate synthase gene. The tree was calculated by neighbor-joining method using MEGA 3.0 software (8). Values of the bootstrap support of the particular branching calculated for 10,000 replicates are indicated at the nodes. The 18 variant sequences obtained in this study were designated by the sample site plus vector species and identification number. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. DL: Dongling, FY: Fuyuan, JL: Jilin; LB: Luobei, MH: Mohe, MS: Mishan; RH: Raohe; SFH: Suifenhe; MDJ: Mudanjiang; HC: Haemaphysalis concinna, Hh: H. longicornis, Ds: Dermacentor silvarum IP: Ixodes persulcatus. Numbers in parentheses indicates the quantity of the same sequences as this strain. GenBank accession numbers of 42 novel sequences are GU935784–GU935790 and HQ396195–HQ396229. The reference strain were the following: China-C-Tt (GQ412339), 96HE158 (NY8) (AY464136), AP-1602 (AF304138), HGE-Webster (AF304136), MD-HGE(AY464132), and Khabarovsk-01 (AY339602).
References
- Dumler JS, Barbet AF, Bekker CP, Dasch GA, Palmer GH, Ray SC, Reorganization of genera in the families Rickettsiaceae and Anaplasmataceae in the order Rickettsiales: unification of some species of Ehrlichia with Anaplasma, Cowdria with Ehrlichia and Ehrlichia with Neorickettsia, descriptions of six new species combinations and designation of Ehrlichia equi and “HGE agent” as subjective synonyms of Ehrlichia phagocytophila. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:2145–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Woldehiwet Z. The natural history of Anaplasma phagocytophilum. Vet Parasitol. 2010;167:108–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cao WC, Zhan L, He J, Foley JE, De Vlas SJ, Wu XM, Natural Anaplasma phagocytophilum infection of ticks and rodents from a forest area of Jilin Province, China. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006;75:664–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhan L, Cao WC, Jiang JF, Zhang XA, Liu YX, Wu XM, Anaplasma phagocytophilum from rodents and sheep, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010;16:764–78.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shpynov S, Fournier PE, Rudakov N, Tarasevich I, Raoult D. Detection of members of the genera Rickettsia, Anaplasma, and Ehrlichia in ticks collected in the Asiatic part of Russia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1078:378–83. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sidelnikov YN, Mediannikov OY, Ivanov LI, Zdanovskaya NI. Clinical and laboratory features of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis in the south of Russian Far East [in Russian]. Epidemiologia i Infectsionnye Bolezni. 2002;3:28–31.
- Inokuma H, Brouqui P, Drancourt M, Raoult D. Citrate synthase gene sequence: a new tool for phylogenetic analysis and identification of Ehrlichia. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:3031–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform. 2004;5:150–63. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Teng KF, Jiang ZJ. Economic insect fauna of China. Fasc 39 Acarina: Ixodidae. Beijing [in Chinese]. Beijing:Science Press, Academia Sinica; 1991. p. 359.