Volume 20, Number 6—June 2014
Letter
Genetic Relatedness of Dolphin Rhabdovirus with Fish Rhabdoviruses
Figure
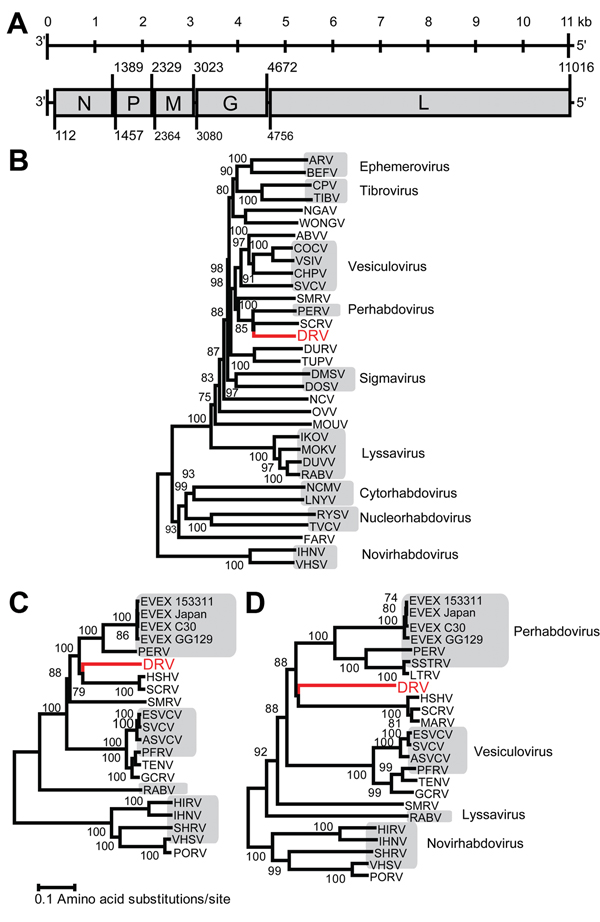
Figure. Genome organization and phylogenetic analysis of dolphin rhabovirus (DRV)A) Genome organization of DRV showing locations of major open reading frames and start and stop codons at the nucleotide levelN, nucleoprotein; P, phosphoprotein; M, Matrix; G, glycoprotein; L, largeB) Phylogenetic neighbor-joining tree with P distances (fraction of positions in which 2 sequences differ) and 1,000 bootstrap replicates of the deduced amino acid sequence of complete DRV L gene protein and members of several Rhabdovirus generaC) Neighbor-joining tree with P distances and 1,000 bootstrap replicates of deduced amino acid sequence of complete DRV L gene protein and those of fish rhabdovirusesD) Neighbor-joining tree with P distances and 1,000 bootstrap replicates of deduced amino acid sequence of complete DRV G gene protein and those of fish rhabdovirusesDRV is indicated in red and bootstrap support values ≥70 are shownLengths of branches are drawn to a scale of amino acid substitutions per site, alignment of several genera was based on a 746-aa segment, and alignment of fish rhabdoviruses was based on a 1,285-aa segment for the L gene and a 227-aa fragment for the G geneGray shading indicates associated genusNucleotide GenBank accession numbers (in parentheses) used to generate phylogenetic trees are as follows: ARV, Adelaide River virus (JN935380); BEFV, bovine ephemeral fever virus (NC_002526); CPV, coastal plains virus (GQ294473); TIBV, Tibrogargan virus (GQ294472); NGAV, Ngaingan virus (NC_013955); WONGV, Wongabel virus (NC_011639); ABVV, American bat vesiculovirus (NC_022755); COCV, Cocal virus Indiana 2 virus (EU373657); VSIV, vesicular stomatitis virus Indiana (NC_001560); CHPV, Chandipura virus (HM627187); SVCV, spring viremia of carp virus (NC_002803); SMRV, Scophthalmus maximus rhabdovirus (HQ003891); PERV, perch rhabdovirus (NC_020803); SCRV, Siniperca chuatsi rhabdovirus (NC_008514); DURV, Durham virus (FJ952155); TUPV, Tupaia virus (NC_007020); DMSV, Drosophila melanogaster sigma virus (AM689309); DOSV, Drosophila obscura sigma virus (GQ410979); NCV, North Creek virus (KF360973); OVV, Oak-Vale virus (JF705876); MOUV, Moussa virus (FJ985749); IKOV, Ikoma lyssavirus (JX193798); MOKV, Mokola virus (NC_006429); DUVV, Duvenhage virus (JN986749); RABV, rabies virus (AF499686); NCMV, northern cereal mosaic virus (NC_002251); LNYV, lettuce necrotic yellows virus (NC_007642); RYSV, rice yellow stunt virus (NC_003746); TVCV, Taro vein chlorosisvirus (NC_006942); FARV, Farmington virus (KC602379); IHNV, infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (L40883); VHSV, viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (AB672614); EVEX 153311, eel virus European X 153311 (FN557213); EVEX Japan, eel virus European X Japan (JX827265); EVEX C30, eel virus European X C30 virus (JN639009); EVEX GG129, eel virus European X GG129 (JN639010); HSHV, hybrid snakehead virus (KC519324); ESVCV, European spring viremia of carp virus (AJ318079); ASVCV, Asian spring viremia of carp virus (DQ097384); PFRV, pike fry rhabdovirus (FJ872827); TENV, Tench rhabdovirus (KC113517); GCRV, grass carp rhabdovirus (KC113518); HIRV, Hirame rhabdovirus (NC_005093); SHRV, snakehead rhabdovirus (NC_000903); PORV, Paralichthys olivaceus rhabdovirus (KC685626); SSTRV, Swedish sea trout rhabdovirus (AAL38523); LTRV, lake trout rhabdovirus (AF434991); MARV, Monopterus albus rhabdovirus (AGZ15720).