Volume 20, Number 8—August 2014
Dispatch
Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus in Ticks Collected from Humans, South Korea, 2013
Figure
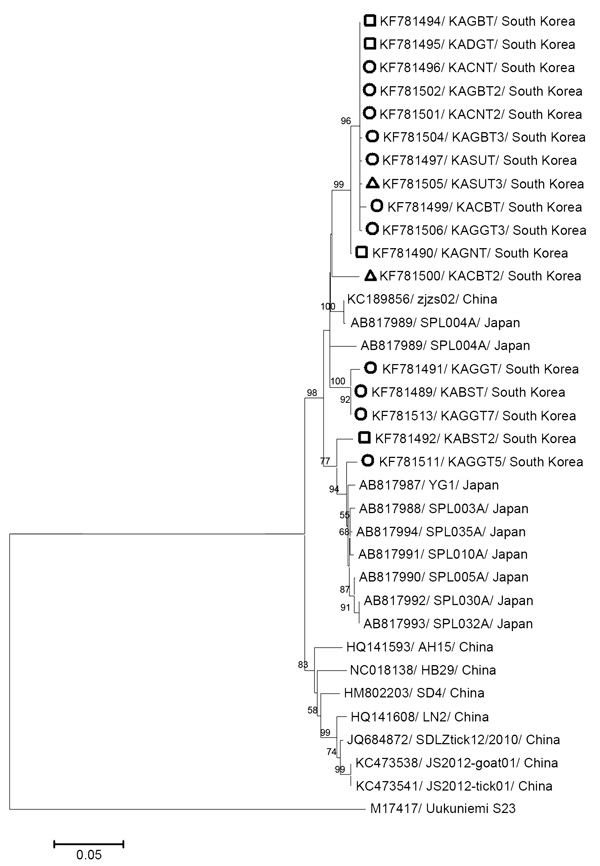
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome viruses based on the partial medium segment sequences (560 bp)The tree was constructed by using the neighbor-joining method based on the p-distance model in MEGA5 (12) (5,000 bootstrap replicates)Uukuniemi virus was used as the outgroupScale bar indicates the nucleotide substitutions per positionAmong the 17 South Korean strains identified in this study, the Korean strains detected from Haemaphysalis longicornis, Amblyomma testudinarium, and Ixodes nipponensis ticks are marked with open circles, squares, and triangles, respectivelyNumbers at nodes indicate bootstrap values.
References
- Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, Liu Y, Li JD, Sun YL, Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1523–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McMullan LK, Folk SM, Kelly AJ, MacNeil A, Goldsmith CS, Metcalfe MG, A new phlebovirus associated with severe febrile illness in Missouri. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:834–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kim K-H, Yi J, Kim G, Choi SJ, Jun KI, Kim N-H, Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:1892–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Takahashi T, Maeda K, Suzuki T, Ishido A, Shigeoka T, Tominaga T, The first identification and retrospective study of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Japan. J Infect Dis. 2014;209:816–27. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- ProMEDmail. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome—South Korea (05): additional fatalities. ProMed. 2013 Jul 6 [cited 2013 Oct 10]. http://www.promedmail.org, archive no. 20130706.1810682.
- Liu Y, Li Q, Hu W, Wu J, Wang Y, Mei L, Person-to-person transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012;12:156–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bao CJ, Guo XL, Qi X, Hu JL, Zhou MH, Varma JK, A family cluster of infections by a newly recognized bunyavirus in eastern China, 2007: further evidence of person-to-person transmission. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:1208–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhang YZ, Zhou DJ, Qin XC, Tian JH, Xiong Y, Wang JB, The ecology, genetic diversity, and phylogeny of Huaiyangshan virus in China. J Virol. 2012;86:2864–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kim HC, Han SH, Chong ST, Klein TA, Choi CY, Nam HY, Ticks collected from selected mammalian hosts surveyed in the Republic of Korea during 2008–2009. Korean J Parasitol. 2011;49:331–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chong ST, Kim HC, Lee IY, Kollars TM Jr, Sancho AR, Sames WJ, Seasonal distribution of ticks in four habitats near the demilitarized zone, Gyeonggi-do (Province), Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 2013;51:319–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yamaguti N, Tipton VJ, Keegan HL, Toshioka S. Ticks of Japan, Korea, and the Ryukyu Islands. Brigham Young Univ Sci Bull Biol Ser. 1971;15:1–226.
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Liu S, Chai C, Wang C, Am S, Lv H, He H, Systematic review of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: virology, epidemiology, and clinical characteristics. Rev Med Virol. 2014;24:90–102. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Savage HM, Godsey MS Jr, Lambert A, Panella NA, Burkhalter KL, Harmon JR, First detection of Heartland virus (Bunyaviridae: Phlebovirus) from field collected arthropods. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013;89:445–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ding F, Zhang W, Wang L, Hu W, Soares Magalhaes RJ, Sun H, Epidemiologic features of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011–2012. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56:1682–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: July 18, 2014
Page updated: July 18, 2014
Page reviewed: July 18, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.