Volume 8, Number 1—January 2002
Research
Antimicrobial Drug Resistance in Pathogens Causing Nosocomial Infections at a University Hospital in Taiwan, 1981-1999
Figure 1
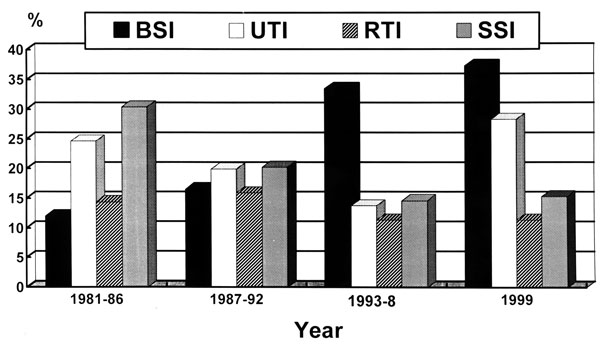
Figure 1. Rates of four major nosocomial infections expressed as number of infections per 10,000 patient-days at National Taiwan University Hospital from 1991 to 1999. BSI, bloodstream infection; UTI, urinary tract infection; SSI, surgical site infection; RTI, respiratory tract infection.
Page created: July 14, 2010
Page updated: July 14, 2010
Page reviewed: July 14, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.