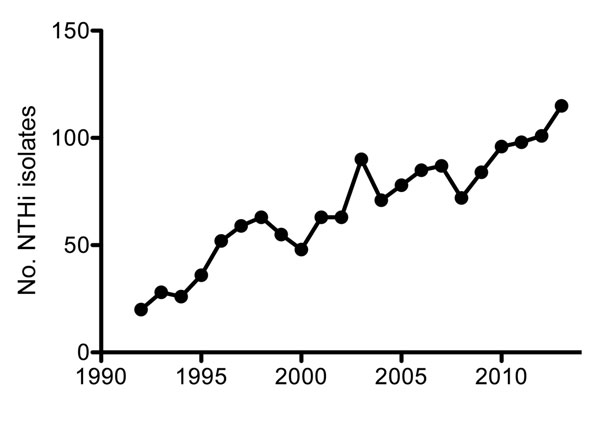
Figure 1. Number of recorded nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) isolates from blood or cerebrospinal fluid in the Netherlands, by year, 1992–2013. Adapted from (6).
Suggested citation for this article
Medscape, LLC is pleased to provide online continuing medical education (CME) for this journal article, allowing clinicians the opportunity to earn CME credit.
This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the Essential Areas and policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education through the joint providership of Medscape, LLC and Emerging Infectious Diseases. Medscape, LLC is accredited by the ACCME to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Medscape, LLC designates this Journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.0 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s)TM. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
All other clinicians completing this activity will be issued a certificate of participation. To participate in this journal CME activity: (1) review the learning objectives and author disclosures; (2) study the education content; (3) take the post-test with a 75% minimum passing score and complete the evaluation at http://www.medscape.org/journal/eid; (4) view/print certificate.
Release date: September 17, 2015; Expiration date: September 17, 2016
Upon completion of this activity, participants will be able to:
• Describe recent evidence supporting the emergence of invasive nontypeable H. influenzae during the last 2 decades
• Discuss mechanisms that may explain the increasing prevalence of invasive nontypeable H. influenzae
• Assess potential strategies to implement effective prevention of invasive nontypeable H. influenzae
Rhonda Ray, PhD, Copyeditor, Emerging Infectious Diseases. Disclosure: Rhonda Ray, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Laurie Barclay, MD, freelance writer and reviewer, Medscape, LLC. Disclosure: Laurie Barclay, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Disclosures: Jeroen D. Langereis, PhD, and Marien I. de Jonge, PhD, have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
The incidence of severe Haemophilus influenza infections, such as sepsis and meningitis, has declined substantially since the introduction of the H. influenzae serotype b vaccine. However, the H. influenzae type b vaccine fails to protect against nontypeable H. influenzae strains, which have become increasingly frequent causes of invasive disease, especially among children and the elderly. We summarize recent literature supporting the emergence of invasive nontypeable H. influenzae and describe mechanisms that may explain its increasing prevalence over the past 2 decades.
Haemophilus influenzae is an extracellular bacterium that commonly colonizes the upper respiratory tract of healthy humans, who are the bacterium’s only known natural reservoir. The H. influenzae species is subdivided into 7 groups, including 6 that express distinct serotypes of polysaccharide capsule (a–f) and 1 unencapsulated group termed nontypeable H. influenzae (NTHi). NTHi is most frequently associated with mild inflammatory diseases of the human mucosa, including otitis media (OM), sinusitis, and exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but it can also cause invasive disease (1). The incidence of invasive NTHi (usually defined as isolation of NTHi from a normally sterile site) has increased substantially since the introduction of the H. influenzae serotype b (Hib) vaccination in the early 1990s and of the Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharide conjugate vaccine (PCV) in the early 2000s (2–5), but factors contributing to NTHi are poorly understood. We summarize data supporting the emergence of NTHi as an increasingly prominent cause of invasive bacterial disease and propose 4 factors that may be driving its rising prevalence worldwide.
We first summarized nationwide surveillance of invasive NTHi disease recorded by the Netherlands Reference Laboratory for Bacterial Meningitis (6). Next, on November 12, 2014, we systematically searched the US National Library of Medicine’s PubMed database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/) by using the search terms “invasive nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae” and “invasive non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae.” We reviewed all papers published during 2000–2014 and summarized all surveillance studies meeting the following criteria: 1) written in English; 2) recording invasive H. influenzae cases occurring during the post-Hib vaccine era; 3) spanning >4 years; and 4) discriminating among serotype b, non–serotype b, and NTHi strains (Table; Technical Appendix). Finally, we described mechanisms that may explain increased prevalence of invasive NTHi infections over the past 2 decades.
Until the mid-1990s, H. influenzae serotype b (Hib) was a predominant cause of invasive disease (e.g., pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis), especially in children. In 1992, a total of 294 (93%) cases with H. influenzae isolates that caused sepsis or meningitis in the Netherlands were attributed to Hib alone. The introduction of an effective vaccine in 1993 drastically decreased the incidence of serotype b infections, which, by 1997, represented only 19 (22%) cases with invasive Haemophilus isolates (6). However, with the near-elimination of invasive disease caused by Hib, the number of recorded invasive NTHi cases increased almost 6-fold during the past 2 decades, from 20 in 1992 to 115 in 2013 (Figure 1). Most (95%) of these NTHi isolates were collected from blood (6). NTHi invasion was detected mainly among persons >50 years of age (80%); Hib was found more often in children <5 years of age, who represented 45% of cases, compared with 38% for those >50 years of age (6). As with the increased number of invasive NTHi cases, a notable increase in the prevalence of non–serotype b encapsulated H. influenzae strains was also observed in the Netherlands (Figure 2), although the number of such cases remains small (6).
Emergence of NTHi as a cause of invasive disease was reported in studies worldwide and was consistently the most prevalent H. influenzae that caused invasive disease (Table). In contrast, Hib cases represented <20% of invasive disease. Seven studies showed a clear increase in absolute numbers of invasive NTHi cases or increased incidence rates of invasive NTHi during the study period (Technical Appendix references 1,7,8,11,15–17); 4 studies showed no increase (Technical Appendix references 2,3,5,6). Large year-to-year differences in overall H. influenzae incidence reported by Laupland et al. make it difficult to interpret whether an increase in invasive NTHi incidence occurred (online Technical Appendix reference 6). Furthermore, a relatively low number of patients (n = 122) over an extended collection period of 7 years complicates the year-to-year analysis in the study by Tsang et al. (Technical Appendix reference 2). However, that study showed a significantly higher mean number of NTHi infections during 2004–2006 (12.7 ± 2.5), compared with the mean number during 2000–2003 (5.0 ± 2.6). Bamberger et al. observed no difference in the incidence of invasive NTHi, perhaps explained by the study population, which consisted of children <15 years of age (online Technical Appendix reference 5). Globally, the average incidence of invasive NTHi is ≈1/100,000 population (4,7,8), a rate similar to that of the Netherlands (9).
Whereas Hib predominantly causes bacterial meningitis in healthy children <5 years of age, most invasive NTHi disease is found in very young children (<20 weeks of age) and the elderly (>65 years). In these populations, NTHi develops as pneumonia or bacteremia without apparent focus of infection (online Technical Appendix references 3,6,16,17). These findings contrast with the widely held view that NTHi infections are mild or asymptomatic. The potential severity of invasive NTHi is illustrated by case fatality rates of 10%–20% (Technical Appendix references 3,6,16), similar to case fatality rates for S. pneumoniae (10).
In addition to the increased incidence of NTHi infections, an increased number of invasive infections caused by encapsulated non–serotype b H. influenzae strains, especially Hie and Hif, has been observed in the Netherlands during the past 2 decades (Figure 2). This trend has been confirmed in multiple independent studies (Technical Appendix references 3,11,17), although the increases are not as large as those observed for NTHi. In Europe, the incidence of non–serotype b H. influenzae capsulated strains was 690 (9%) of 7,992 isolates; 500 (72.5%) of the 690 isolates were Hif, and 143 (20.7%) were Hie (Technical Appendix reference 3). This distribution of non–serotype b H. influenzae encapsulated serotypes causing invasive disease was similar in other parts of the world, except for specific ethnic groups where Hia is most prevalent (11–13). The epidemiology and clinical manifestations of invasive Hie and Hif strains are similar to that of NTHi and mostly occur as pneumonia or bacteremia in the elderly (14). In contrast, invasive Hia infections are more similar to Hib infections than to NTHi infections. Hia infections occurred mainly in young children and frequently as meningitis (12,13). The apparent similarity between Hia and Hib might be attributed to similarities in capsule structure; both contain a neutral sugar, an alcohol (ribitol), and a phosphodiester (15).
Although numbers of NTHi cases are increasing, underlying mechanisms for the increase are yet to be determined. We offer 4 possible explanations for the emergence of NTHi as a pathogen causing invasive disease.
The success of the Hib vaccine and PCV is attributed to the strong immunogenic properties of polysaccharide conjugate formulations. However, protection against H. influenzae is limited to serotype b, and the possibility exists that another disease, caused by other H. influenzae strains against which vaccines offer no protection, may replace Hib. In fact, already in 1997, Marc Lipsitch anticipated the possibility of strain replacement with the introduction of the Hib vaccine (16). The significance of strain replacement remains controversial: some clinical studies highlight its potential danger (2,4); others fail to observe it altogether (8,17). Besides the introduction of the Hib vaccination, introduction of the PCV has also been proposed as contributing to H. influenzae strain replacement. Multiple studies show substantial increases in NTHi nasopharyngeal colonization (3,5) and in percentage of OM cases caused by NTHi in PCV-vaccinated persons (18–20). This increased nasopharyngeal carriage of NTHi in PCV-vaccinated children might increase transmission to groups susceptible to invasive NTHi disease, such as the elderly, and might thereby contribute to the emergence of invasive NTHi disease. Strain replacement during colonization of persons >65 years of age appears to lack investigation, possibly because of the relatively low percentage of nasopharyngeal carriage in this age group. However, NTHi carriage rates in parents of PCV-vaccinated children increased from 23% prevaccination to 40% postvaccination (5), indicating that carriage of NTHi has increased in healthy adults, possibly because of increased transmission from PCV-vaccinated children. Increased NTHi carriage might contribute to the increased number of invasive NTHi disease cases recorded during the past 20 years.
Whether the emergence of NTHi as a cause of invasive disease indicates an actual increase in the number of cases or results from improved detection and serotyping is difficult to assess. Bacterial culture is the gold standard for H. influenzae detection. However, a major disadvantage of culture is that multiple days are needed to isolate bacteria and confirm culture identity. Therefore, rapid and more sensitive real-time PCR (rtPCR) assays have been developed to shorten the time needed for identification. Several rtPCR assays that target different H. influenzae genes have been developed and are more sensitive for detecting the hpd gene than for detecting genes ompP2 or bexA (detection of capsulated H. influenzae strains only) (21). Despite evidence that rtPCR-based assays provide improved detection of H. influenzae, all studies we summarize use bacterial culture as the detection method (Table).
Slide agglutination is the gold standard for serotyping H. influenzae in most laboratories, although this technique is prone to misinterpretation because of nonspecific agglutination, cross-reactions, or autoagglutination. The transition from slide-agglutination to PCR-based methods that detect capsule locus genes, such as bexA or bexB, has substantially improved the accuracy of serotyping results. For instance, Kastrin et al. recently showed that 80 isolates originally serotyped as NTHi were detected as unencapsulated by PCR, but 12 (11% of total isolates) of 28 isolates reported as capsulated by slide agglutination were shown by PCR to harbor no functional capsule genes (7). On the basis of PCR results, 5%–20% of strains typed by slide agglutination were mistyped as encapsulated (7,22,23). Although PCR detection methods apparently detect more invasive NTHi isolates than does slide agglutination, the increased detection by PCR does not explain the year-to-year increase in number of invasive NTHi cases (Table) because, within each study, similar typing techniques were used throughout the study period. However, the number of invasive NTHi cases likely is underrepresented in studies that use slide agglutination for detection.
Increased bacterial virulence as a consequence of the acquisition of novel virulence factors might also contribute to invasive NTHi disease. The natural genetic competence of NTHi enables the exchange of large pieces of DNA between strains at a high frequency (24), a process that supports acquisition of novel virulence factors.
Because invasive infection and death of host do not enhance transmissibility of virulent NTHi, the evolutionary basis for these genetic changes may lie in fitness advantages during nasopharyngeal colonization, a theory supported by recent studies. For instance, we have shown that NTHi isolates collected from middle ear fluid of children with OM exhibited increased resistance to complement-mediated killing compared with colonizing NTHi isolates from the nasopharynx (25), but we found that colonizing and OM-causing NTHi strains with a similar multilocus sequence type collected from the same patient showed no difference in complement resistance (26). This similarity in complement resistance for NTHi strains with a similar multilocus sequence type indicates that NTHi strains had already acquired mechanisms that increased resistance to complement-mediated killing during colonization and retained them during translocation to the middle ear cavity. These observations were corroborated by a later study that showed that most of the phase-variable genes known to modulate resistance to complement-mediated killing were regulated similarly for colonizing and OM-causing NTHi strains within the same patient (27).
Limited data are available on the mechanisms that underlie increased NTHi virulence in patients with invasive disease. Recently, Bajanca-Lavado et al. showed that an NTHi strain that caused endocarditis appeared highly virulent because of the expression of a second copy of the IgA protease gene (igaB) combined with a strong resistance to complement-mediated killing (28). We have shown that NTHi strains collected from patients with invasive disease more frequently incorporate galactose to heptose III in the lipooligosaccharide; this modification decreases binding of IgM and thereby increases resistance to complement-mediated killing (29). A study by Hällstrom et al. showed a correlation between complement resistance and disease severity but no difference in complement resistance between invasive and colonizing NTHi strains (30). This lack of difference in complement resistance between invasive and colonizing NTHi strains might be explained by the large proportion (41%) of patients with immune deficiencies in the invasive group, therefore potentially reducing the immunologic pressure for NTHi strains to maintain complement resistance in the bloodstream.
That the type b capsule protects H. influenzae from the bactericidal activity of the complement system and that this protection contributes to its invasive character are generally accepted ideas. Zwahlen et al. reported that capsule transformants showed dramatic differences in virulence (31). Although all capsule types were able to colonize the nasopharynx of rats, bacteremia was detected only in animals challenged with serotypes a and b and with a single animal serotype, f. The highest bacterial load was found among animals infected with serotype b. Therefore, losing the protective capsule would be expected to render H. influenzae unable to cause invasive disease. However, recent whole genome sequencing results showed that a few invasive NTHi isolates had a multilocus sequence type usually associated with serotype b strains (32). In these NTHi isolates, lack of capsule expression was related to the deletion of the bexA gene, whereas the remaining capsule locus was similar to that of the corresponding capsulated isolates. However, the lack of a capsule did not abrogate the ability of these particular NTHi strains to cause invasive disease, indicating that other factors besides the capsule of Hib strains contribute to invasiveness. For example, Fleury et al. found that a Hib- and Hif-specific lipoprotein PH was able to bind human factor H, resulting in increased resistance to complement-mediated killing (33). Identification of other genetic factors might partly explain why NTHi is found to cause invasive disease.
The epidemiology of invasive H. influenzae disease has changed dramatically over the past 20 years (2,7). Instead of being mainly a pediatric disease caused by Hib, formerly rare capsular serotypes (mostly Hia and Hif) and NTHi cause most of invasive H. influenzae cases, especially among the elderly (Table). For instance, in the United States, 78% of invasive H. influenzae cases among adults >65 years of age were attributed to NTHi, with an even higher frequency (89%) among those >85 years of age (34).
Reasons for this apparent increase in susceptibility to invasive NTHi infections in the elderly are unknown, but the immunologic status of the host is believed to play a role. Coexisting conditions or risk factors such as coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, and smoking were more common in patients with invasive disease compared with the general population (34). The number of patients with COPD, the third leading cause of death worldwide (35), is increasing. NTHi is often found colonizing the lungs of patients with COPD, and the increased number of patients with COPD might contribute to the increased incidence of invasive NTHi cases. Serum IgG levels to H. influenzae protein D showed a tendency to decline with age but were even lower in adults with coexisting conditions such as COPD, cancer, chronic renal failure, or diabetes, compared with age-matched healthy persons (36). The absence of naturally acquired antibodies against protein D, a highly conserved antigen, may contribute to increased susceptibility to invasive NTHi disease. However, invasive NTHi infections are found not only in persons with immunocompromising conditions (e.g., chronic lymphatic leukemia or multiple myeloma) or coexisting conditions (e.g., COPD, diabetes, or cardiovascular diseases) but in almost half of cases in persons who were otherwise in good health (Technical Appendix references 6,11).
Recently, several groups have found that binding of IgM to the bacterial surface might play a role in the innate defense against NTHi infections (25,29,37). This finding is corroborated by a clinical study in which Micol et al. showed that patients with hyper-IgM syndrome were less susceptible to NTHi colonization, a finding that emphasizes the role of IgM in the immune defense against this pathogen (38). The percentages of IgM-producing CD27+ memory B cells in the peripheral blood of children are low but increases to almost 20% in adults and declines again in the elderly (39). These findings correspond with levels of susceptibility to bacterial infections such as NTHi in young children and the elderly. Studies examining serum immunoglobulin levels in patients with invasive NTHi disease compared with those of healthy age-matched patients could help address the question of whether a diminished protective immunoglobulin level in the elderly contributes to susceptibility to invasive NTHi disease.
Besides impaired humoral immunity, diminished cellular immunity has been described in the elderly. Evidence exists for a broad, age-related alteration in the development and function of lymphocytes, monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils (40), although specific effects of these changes on susceptibility to invasive NTHi infections have not been investigated in detail. Recently, we showed that neutrophils efficiently phagocytose and kill opsonized NTHi bacteria (29), but decreased neutrophil phagocytic capacity among the elderly may impair this host defense and contribute to poorer clinical outcomes during NTHi infection.
From examination of the available literature, we conclude that invasive NTHi disease is emerging worldwide and demands implementation of effective prevention. Development of vaccines against NTHi is considered paramount because this pathogen is also often found to cause pneumonia in patients with COPD and OM in children. However, development of an effective vaccine for risk groups demands knowledge about factors that contribute to the emergence of invasive NTHi disease. Age and coexisting conditions are likely predisposing factors for invasive NTHi infections. Also, increased NTHi colonization in children might contribute to increased transmission to persons susceptible to developing invasive NTHi disease. In view of these factors, broad vaccination strategies for the general public could be effective by decreasing transmission, bolstering herd immunity, and protecting potentially susceptible persons.
Dr. Langereis is a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Pediatrics, Laboratory of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands. His research interest includes the pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae.
Dr. de Jonge is head of the Laboratory of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, Radboud University Medical Center, and focuses on viral and bacterial respiratory infections in children.
We thank Chris Hergott and Dr. Lorelei Verbeek for their critical reading of this manuscript.
Suggested citation for this article: Langereis JD, de Jonge MI. Invasive disease caused by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015 Oct [date cited]. http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid2110.150004
To obtain credit, you should first read the journal article. After reading the article, you should be able to answer the following, related, multiple-choice questions. To complete the questions (with a minimum 75% passing score) and earn continuing medical education (CME) credit, please go to http://www.medscape.org/journal/eid. Credit cannot be obtained for tests completed on paper, although you may use the worksheet below to keep a record of your answers. You must be a registered user on Medscape.org. If you are not registered on Medscape.org, please click on the “Register” link on the right hand side of the website to register. Only one answer is correct for each question. Once you successfully answer all post-test questions you will be able to view and/or print your certificate. For questions regarding the content of this activity, contact the accredited provider, CME@medscape.net. For technical assistance, contact CME@webmd.net. American Medical Association’s Physician’s Recognition Award (AMA PRA) credits are accepted in the US as evidence of participation in CME activities. For further information on this award, please refer to http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/about-ama/awards/ama-physicians-recognition-award.page. The AMA has determined that physicians not licensed in the US who participate in this CME activity are eligible for AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™. Through agreements that the AMA has made with agencies in some countries, AMA PRA credit may be acceptable as evidence of participation in CME activities. If you are not licensed in the US, please complete the questions online, print the certificate and present it to your national medical association for review.
Article Title:
Invasive Disease Caused by Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae
1. You are consulting for a large health maintenance organization regarding planning strategies to deal with invasive nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. According to the review by Langereis and colleagues, which of the following statements about recent evidence regarding the emergence of invasive nontypeable H. influenzae is correct?
A. The number of recorded cases doubled in the last 2 decades
B. Nontypeable H. influenzae invasion was detected mainly in adolescents
C. Nontypeable H. influenzae invasion develops as a pneumonia or bacteremia without apparent focus of infection
D. Emergence of nontypeable H. influenzae as a cause of invasive disease is restricted to The Netherlands
2. According to the review by Langereis and colleagues, which of the following statements about mechanisms that may explain the increasing prevalence of invasive nontypeable H. influenzae is correct?
A. Use of the Hib vaccine and polysaccharide conjugate vaccine do not affect H. influenzae strain replacement
B. The emergence of nontypeable H. influenzae as a cause for invasive disease is solely the result of an increase in the number of disease cases
C. Increased bacterial virulence is not a proposed mechanism contributing to invasive nontypeable H. influenzae
D. The epidemiology of nontypeable H. influenzae has changed dramatically in the last 20 years, now affecting mostly elderly persons, perhaps because of increased comorbidity compromising immunologic status
3. According to the review by Langereis and colleagues, which of the following statements about potential strategies to implement effective prevention of invasive nontypeable H. influenzae would most likely be correct?
A. Development of vaccines against nontypeable H. influenzae is not likely to play a significant role
B. Development of an effective vaccine for risk groups demands clarification of the factors contributing to the emergence of invasive nontypeable H. influenzae disease, such as age and comorbidity
C. Reducing nontypeable H. influenzae colonization in children is unlikely to help prevent invasive disease
D. Broad vaccination strategies in the general public are unlikely to help prevent invasive nontypeable H. influenzae in those at greatest risk
|
1. The activity supported the learning objectives. |
||||
|
Strongly Disagree |
|
|
|
Strongly Agree |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
2. The material was organized clearly for learning to occur. |
||||
|
Strongly Disagree |
|
|
|
Strongly Agree |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
3. The content learned from this activity will impact my practice. |
||||
|
Strongly Disagree |
|
|
|
Strongly Agree |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
4. The activity was presented objectively and free of commercial bias. |
||||
|
Strongly Disagree |
|
|
|
Strongly Agree |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |

Figure 1. Number of recorded nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) isolates from blood or cerebrospinal fluid in the Netherlands, by year, 1992–2013. Adapted from (6).
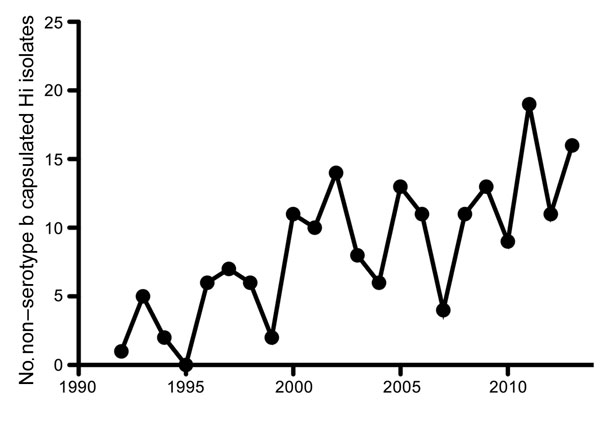
Figure 2. Number of recorded non–serotype b capsulated Haemophilus influenzae (Hi) isolates from blood or cerebrospinal fluid in the Netherlands, by year, 1992–2013. Adapted from (6).
Invasive Haemophilus influenzae cases worldwide since introduction of serotype b vaccine*
| Location | Period of strain collection | Surveillance method | Typing method | Changes in NTHi cases or incidence† | Serotyped Hi isolates, no. | Serotype b isolates, % | Non–serotype b isolates, % | NTHi isolates, % | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canada | 1989–2007 | Active, prospective surveillance | SA | Increased incidence | 1,455 | 20 | 17 | 62 | (1) |
| Canada | 2000–2006 | Nationwide surveillance | SA+PCR | No change | 122 | 4 | 39 | 57 | (2) |
| Europe | 1996–2006 | European Union Invasive Bacterial Infection Surveillance | SA or PCR | No change | 7,992 | 35 | 9 | 56 | (3) |
| Germany | 2001–2004 | Nationwide surveillance | Not reported | NA | 147 | 40 | 14 | 46 | (4) |
| Israel‡ | 2003–2012 | Nationwide prospective surveillance | SA | No change | 389 | 26 | 11 | 62 | (5) |
| Multiple§ | 2000–2008 | Active population-based surveillance | Not reported | No change | 398 | 6 | 17 | 77 | (6) |
| Portugal | 2002–2010 | Laboratory-based passive surveillance | PCR | Increased cases | 144 | 13 | 10 | 77 | (7) |
| Slovenia | 2000–2008 | National surveillance | PCR | Increased incidence | 108¶ | 13 | 2 | 85 | (8) |
| Spain | 2004–2009 | Nationwide surveillance | PCR | NA | 307 | 5 | 8 | 87 | (9) |
| Spain | 2008–2013 | Laboratory-based study | SA | NA | 70 | 1 | 14 | 85 | (10) |
| Sweden | 1997–2009 | Retrospective laboratory-based study | PCR | Increased cases or incidence | 268# | 11 | 18 | 71 | (11) |
| Taiwan | 1999–2002 | National surveillance | SA | NA | 10 | 20 | 0 | 80 | (12) |
| USA, Alaska | 1991–1996 | Active surveillance | SA | NA | 40 | 14 | 31 | 54 | (13) |
| USA, Arkansas | 1993–2001 | Retrospective laboratory-based study | SA | NA | 33 | 3 | 6 | 91 | (14) |
| USA, Utah | 1998–2008 | Passive surveillance | SA | Increased cases or incidence | 101 | 9 | 49 | 43 | (15) |
| USA, Illinois | 1996–2004 | Passive surveillance | SA | Increased incidence | 522 | 15 | 31 | 54 | (16) |
| USA | 1999–2008 | Active surveillance | SA | Increased incidence | 4190 | 4 | 26 | 70 | (17,18) |
*Hi, Haemophilus influenzae; NA, not applicable due to limited sample size (<100 isolates) or lack of year-to-year data; NTHi, nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae; Ref, reference (see online Technical Appendix, http://wwwnc.cdc.gov/EID/article/21/10/15-0004-Techapp.pdf); SA, slide agglutination; SA+PCR, slide agglutination positive isolates confirmed by PCR.
†Increased cases = increase in number of NTHi cases in patients >1 years of age; Increased incidence = increase in NTHi incidence rate in patients >1 year of age; No change = no difference in number or incidence rate of NTHi cases.
‡Pediatric cases (<15 years of age) only.
§Australia, Canada, and Denmark.
¶PCR-typed isolates from post-Hib vaccination era only.
#PCR-typed isolates only.
*