Volume 13, Number 5—May 2007
Letter
Acetobacter cibinongensis Bacteremia in Human
Figure
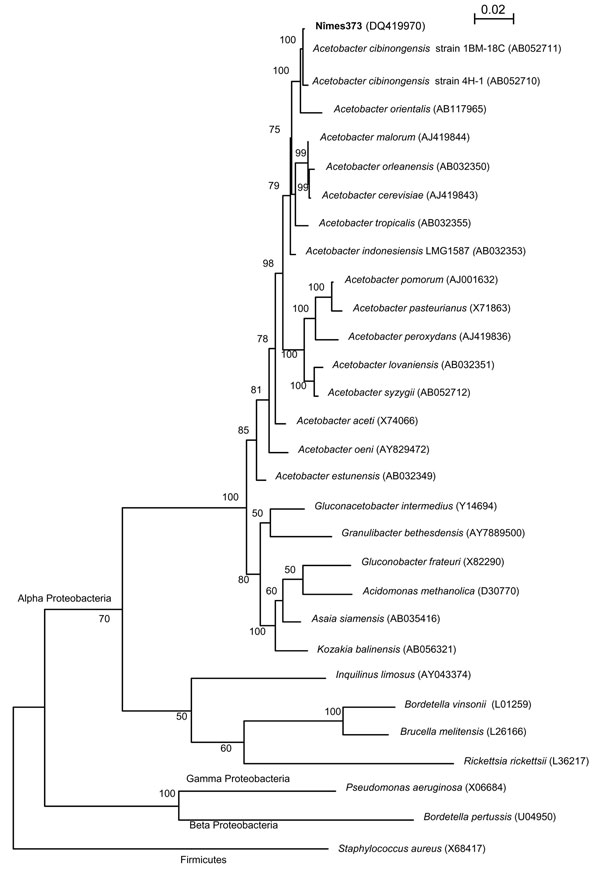
Figure. 16S rDNA maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree showing the relationships of the isolate nîmes373 with 15 species of the genus Acetobacter and 6 strains representative of the 6 other genera of acetic acid bacteria in the Alpha Proteobacteria. Sequences of Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Proteobacteria of clinical relevance were also included in the tree. Staphylococcus aureus (Firmicutes) 16S rDNA was used as an outgroup. The 16S rDNA sequences used to reconstruct this tree were obtained from the GenBank database, and their accession numbers are indicated in brackets. The tree was reconstructed using DNAML from the PHYLIP package v. 3.6.6, on the basis of the F84 (+ gamma distribution + invariant sites) substitution model. The scale bar indicates 0.02 substitutions per nucleotide position. Numbers given at the nodes represent bootstrap percentages calculated on 100 replicates.