Volume 14, Number 7—July 2008
Research
Transmission of Bartonella henselae by Ixodes ricinus
Figure 2
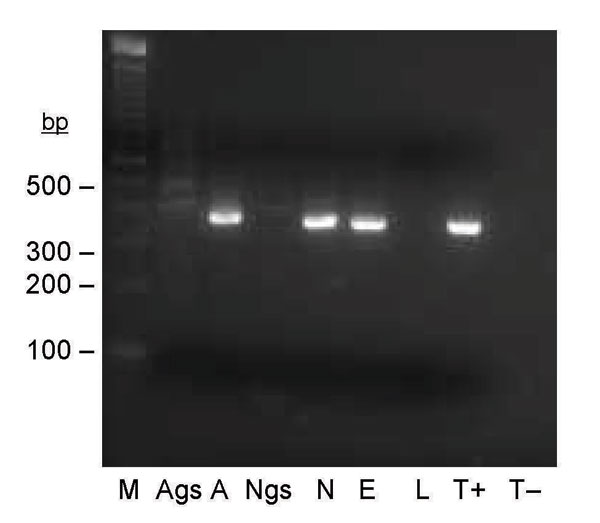
Figure 2. Seminested PCR detection of Bartonella spp. DNA in Ixodes ricinus ticks fed on B. henselae–infected ovine blood at preceding stage. Lane M, 100-bp DNA molecular mass marker; lane Ags, salivary glands of a female adult fed on infected blood as a nymph; lane A, carcass of a female adult fed on infected blood as a nymph; lane Ngs, salivary glands of a nymph fed on infected blood as a larva; lane N, carcass of a nymph fed on infected blood as a larva; lane E, eggs laid by female adult fed on infected blood; lane L, larvae hatched from female adult fed on infected blood; lane T+, B. bacilliformis DNA; lane T–, nymph fed on uninfected ovine blood.
Page created: July 12, 2010
Page updated: July 12, 2010
Page reviewed: July 12, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.