Volume 18, Number 4—April 2012
Peer Reviewed Report Available Online Only
Multidisciplinary and Evidence-based Method for Prioritizing Diseases of Food-producing Animals and Zoonoses
Figure 1
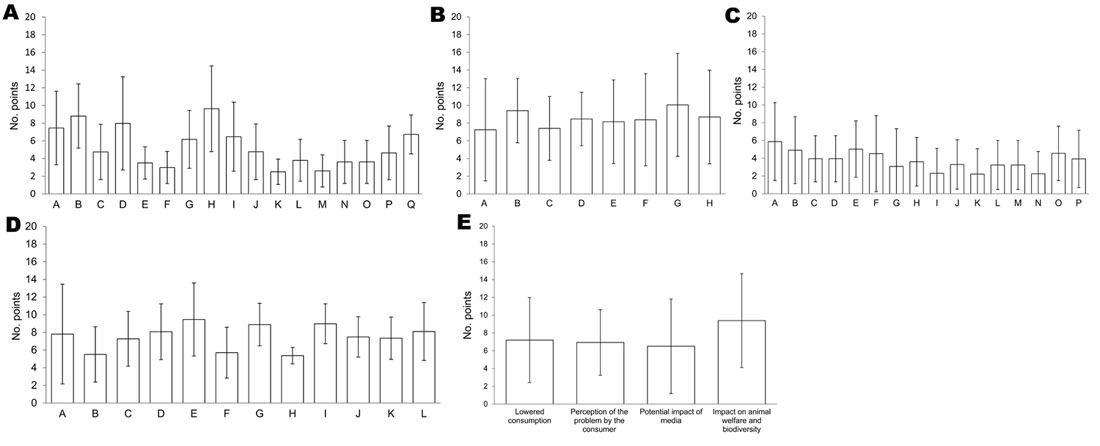
Figure 1. Weighting (mean no. points) of criteria for diseases of food-producing animals and zoonoses for 5 aspects of a pathogen proposed by experts, Europe. A) Epidemiology by 18 experts. A, illness rate; B, case-fatality rate; C, specificity of agents; D, mode of transmission; E, incubation period; F, clinical course; G, environmental persistence; H, epizootic potential; I, evolutive potential; J, cattle; K, small ruminants; L, swine; M, equines; N, poultry; O, lagomorphs; P, wildlife; Q, vector(s) or reservoir(s) in the European Union. B) Prevention/control by 16 experts. A, control of reservoir(s)/vector(s); B, vaccination; C, treatment; D, availability/quality of diagnostic tools; E, knowledge of pathogen; F, effectiveness of control; G, effectiveness of prevention; H, surveillance of pathogen. C) Economy/trade by 14 experts. A, loss of productivity; B, costs of mandatory slaughtering; C, costs of treatment and disinfection; D, costs of vaccination; E, limitation of importation-exportation; F, disturbance of supply/demand; G, impact on related sectors; H, impact on cattle industry; I, impact on small ruminants industry; J, impact on swine industry; K, impact on equine industry; L, impact on poultry industry; M, impact on rabbit industry; N, impact on wildlife industry; O, zoonotic impact (cost of illness); P, zoonotic impact (cost of prevention). D) Public health by 10 experts. A, zoonotic/common agent; B, classification of zoonoses; C, disease knowledge in humans; D, illness rate; E, case-fatality rate; F, contamination route; G, after effects; H, existing control plan; I, epidemic potential; J, vaccination; K, treatment; L, availability and quality of diagnostic tools. E) Society by 13 experts. Error bars indicate ± SD.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.