Volume 19, Number 10—October 2013
Dispatch
Variant Human T-cell Lymphotropic Virus Type 1c and Adult T-cell Leukemia, Australia
Figure 2
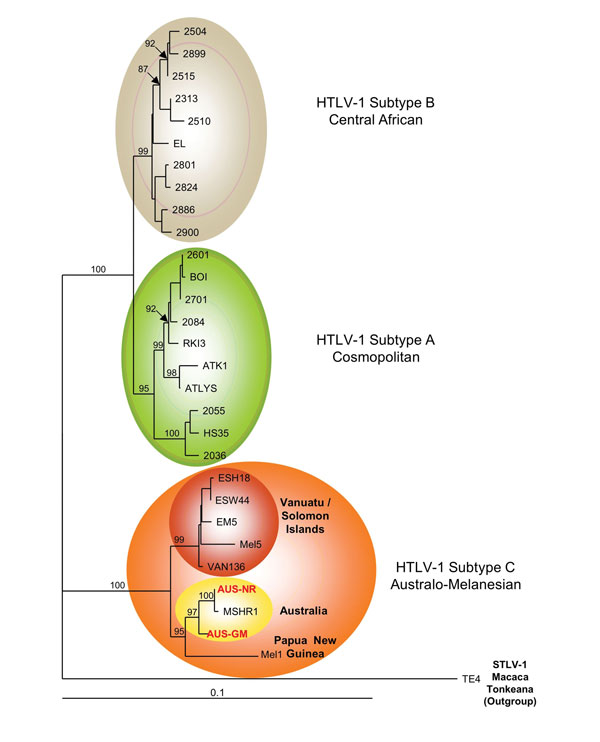
Figure 2. . Phylogenetic tree generated on a 1,386-bp fragment of the env gene for 30 primate T-lymphotropic virus type 1 available sequences, including the 2 sequences generated in this work (in red boldface). The lymphotropic virus type 1 strains were aligned with the DAMBE program (version 4.2.13). The final alignment was submitted to the ModelTest program (version 3.6) to select, according to the Akaike Information Criterion, the best model to apply to phylogenetic analyses. The selected model was the Tamura Nei. Bootstrap values were calculated for 1,000 replicates, and the numbers at some nodes of the tree (bootstrap values) indicate frequencies of occurrence for 100 trees. The TE4 strain from Macaca tonkeana macaques was used as an outgroup. The branch lengths are drawn to scale, and the scale bar indicates nucleotide replacements per site. Three of the 4 major HTLV-1 subtypes are shown. Subtype c corresponds to Australo-Melanesian HTLV-1c and includes the 2 env sequences (Aus-NR and Aus-GM; GenBank accession nos. KF242508 and KF242509, respectively), which were obtained from patients 1 and 2, respectively. HTLV, human T-lymphotropic virus; STLV, simian T-lymphotropic virus.
1These authors equally contributed to this article.