Volume 19, Number 9—September 2013
Letter
Alaria alata Infection in European Mink
Figure
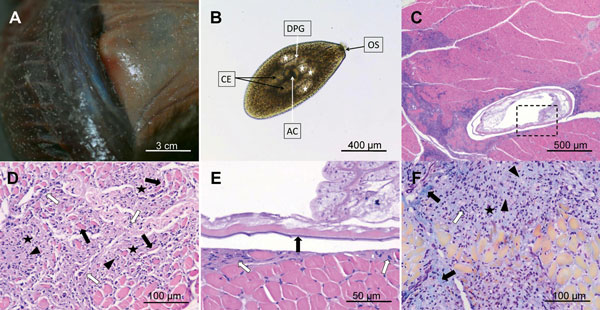
Figure. . Lesions produced by mesocercariae of Alaria alata in European mink. A) Mesocercariae in the muscle and subcutaneous tissue produce whitish, round or slightly oval, well-defined nodules. B) Free mesocercarium after artificial digestion, showing the characteristics of A. alata mesocercarium: piriform body with anterior oral sucker (OS), acetabulum (AC) positioned in the center of the parasite, 2 pairs of large, finely granulated penetration glands (white stars), limiting the anterior part of the acetabulum, linear ducts of penetration glands (DPG) converging to the oral opening of the oral sucker and large double ceca placed posterior to the acetabulum. C) Histologic section showing an encysted mesocercarium in the muscle (parasite is surrounded by a capsule and pericystic inflammation, which extends to the surrounding muscular tissue). D) Mononuclear leucocytes (arrowheads) scattered between the fibroblastic proliferations (white arrows) and collagen deposits (black stars). Muscle fibers are atrophic due to compression (black arrows). E) Microscopic detail of the inset from panel C. Some mesocercariae (indicated by black arrow) are enclosed in a thin, pale staining capsule (white arrows). Note the lack of leukocyte response. F) Migration route of the parasite (route with center marked by the black star), followed by invasion of nonnecrotic muscle fibers by mononucleate inflammatory cells (white arrow) located mainly in the center of the migration tract and fibrous connective tissue with collagen fibers densely packed at the periphery (bright green, marked by black arrows) and more loosely in the center (pale green material, marked by arrowheads). Hematoxylin–eosin stain (panels C, D, E); Masson trichrome (panel F); original magnifications x40 (panels B and C), x200 (panels D and F), and x400 (panel E).