Isolation of MERS Coronavirus from a Dromedary Camel, Qatar, 2014
V. Stalin Raj
1, Elmoubasher A.B.A. Farag
1, Chantal B.E.M. Reusken, Mart M. Lamers, Suzan D. Pas, Jolanda Voermans, Saskia L. Smits, Albert D.M.E. Osterhaus, Naema Al-Mawlawi, Hamad E. Al-Romaihi, Mohd M. AlHajri

, Ahmed M. El-Sayed, Khaled A. Mohran, Hazem Ghobashy, Farhoud Alhajri, Mohamed Al-Thani, Salih A. Al-Marri, Mamdouh M. El-Maghraby, Marion P.G. Koopmans, and Bart L. Haagmans

Author affiliations: Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands (V. Stalin Raj, C.B.E.M. Reusken, M.M. Lamers, S.D. Pas, J. Voermans, S.L. Smits, A.D.M.E. Osterhaus, M.P.G. Koopmans, B.L. Haagmans); Supreme Council of Health, Doha , Qatar (E.A.B.A. Farag, H.E. Al-Romaihi, M.M. AlHajri, A.M. El-Sayed, M. Al-Thani, S.A. Al-Marri); Hamad Medical Corporation, Doha (N. Al-Mawlawi); Ministry of Environment, Doha (K.A. Mohran, H. Ghobashy, F. Alhajri, M.M. El-Maghraby)
Main Article
Figure 2
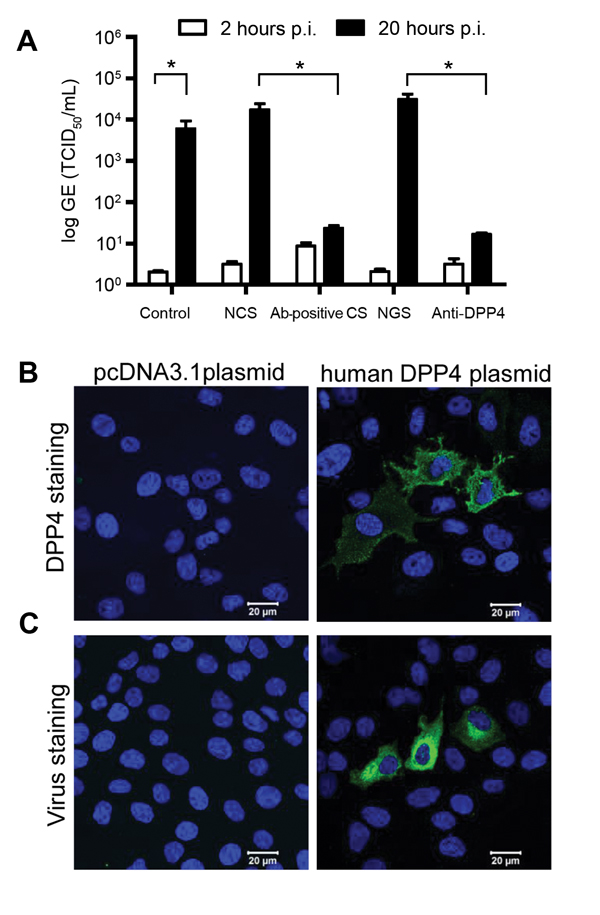
Figure 2. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) from camel replicates in human hepatoma (Huh-7) cells and uses human DPP4 as entry receptorHuh-7 cells were inoculated with camel MERS-CoV and left for 1 hNext, cells were washed twice, and supernatant was collected at 2 h (open bars) and 20 h (closed bars) before being tested for MERS-CoV RNA by using a TaqMan assayWe analyzed control camel MERS-CoV–infected cells, cells inoculated with camel MERS-CoV in the presence of normal camel serum (NCS), MERS-CoV–antibody positive camel serum (Ab-positive CS), normal goat serum (NGS), and anti-DPP4 polyclonal antibody–treated cellsResults are expressed as genome equivalents (GE), 50% tissue culture infective dose (TCID50/mL) (A)MDCK cells transfected with plasmid-encoding human DPP4 or a control plasmid (pcDNA) were stained with polyclonal antibody against human DPP4 (B) or inoculated with camel MERS-CoV and fixed 20 h after inoculation (p.i.) and stained for viral antigen (C).
Main Article
Page created: July 18, 2014
Page updated: July 18, 2014
Page reviewed: July 18, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
