Volume 18, Number 11—November 2012
Dispatch
Seroprevalence of Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 Virus Antibody, England, 2010 and 2011
Figure 2
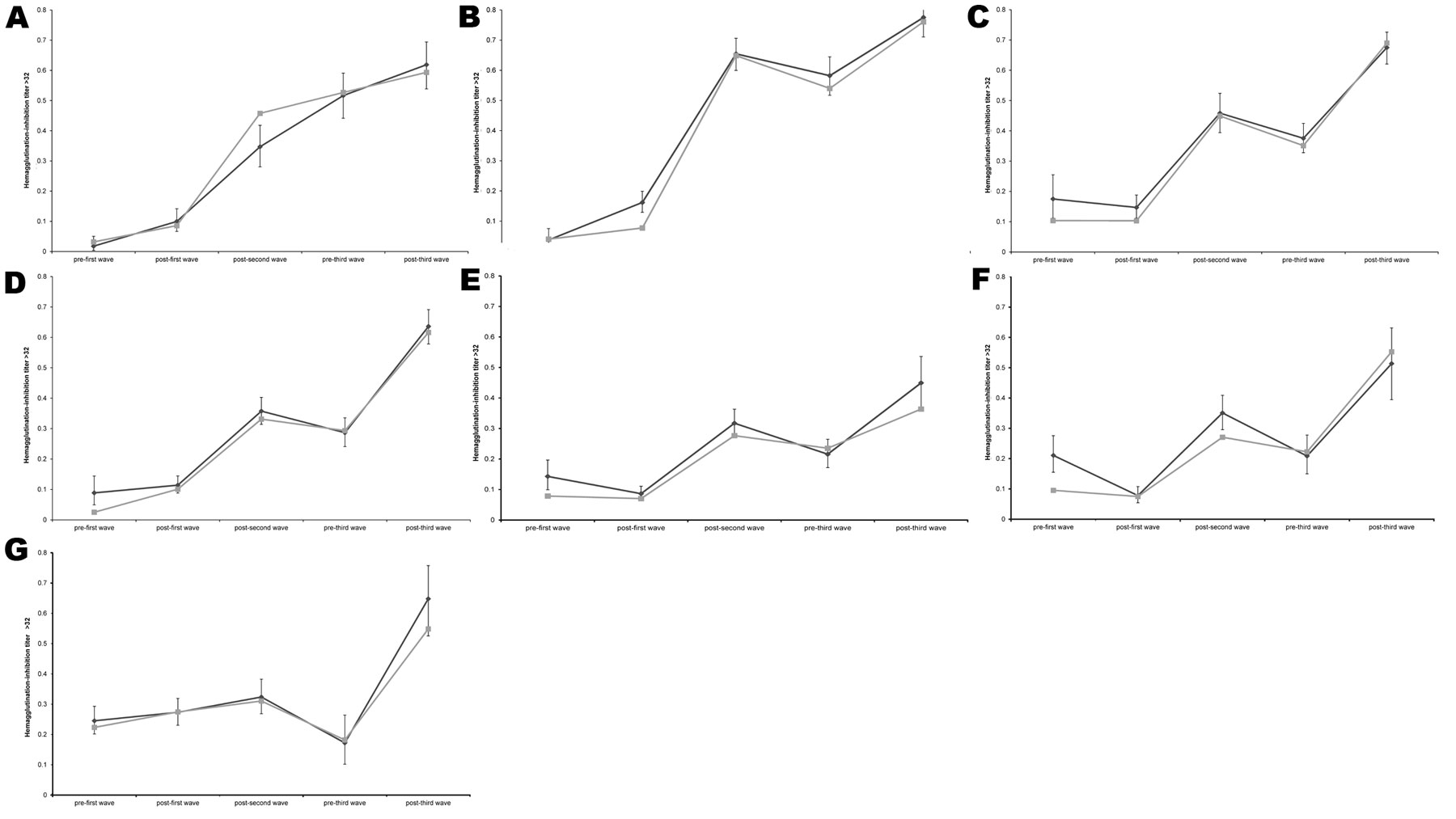
Figure 2. . . . . . Percentage of samples with hemagglutination-inhibition titer >32 during consecutive waves of influenza activity, England, summer 2009 and 2009-10 and 2010-11 influenza seasons. Data were plotted from all available results determined by hemagglutination-inhibition assay on samples from all regions. A) Children <5 years old. B) Children 5–14 years old. C) Persons 15–24 years old. D) Persons 25–44 years old. E) Persons 45–64 years old. F) Persons 65–74 years old. G) Persons >75 years old. Black line, results from all regions; gray line, results from the North West and South West regions, which provided samples throughout the entire period. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals.
Page created: October 05, 2012
Page updated: October 05, 2012
Page reviewed: October 05, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.