Volume 18, Number 9—September 2012
CME ACTIVITY - Policy Review
Control of Fluoroquinolone Resistance through Successful Regulation, Australia
Figure 2
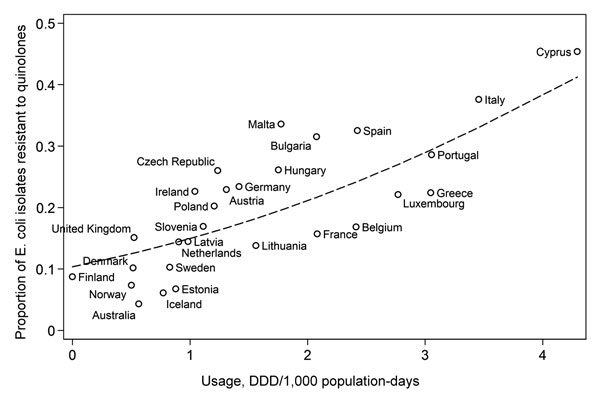
Figure 2. . . Quinolone use data for Europe from the European Surveillance of Antimicrobial Consumption initiative for antibiotic use in ambulatory care settings and European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System. Use data for Australia from the Australian Group on Antibiotic Resistance (community isolates) and Drug Utilization Sub-Committee Drug Utilization Database (Commonwealth of Australia). Line represents logit-modeled relationship between resistance and usage, weighted by number of isolates tested. Usage rate calculated on the basis of medication use of 1,000 persons per day. DDD, defined daily dose; E. coli, Escherichia coli.
Page created: August 17, 2012
Page updated: August 17, 2012
Page reviewed: August 17, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.