Volume 19, Number 2—February 2013
Dispatch
Genetic Variants of Echovirus 13, Northern India, 2010
Figure
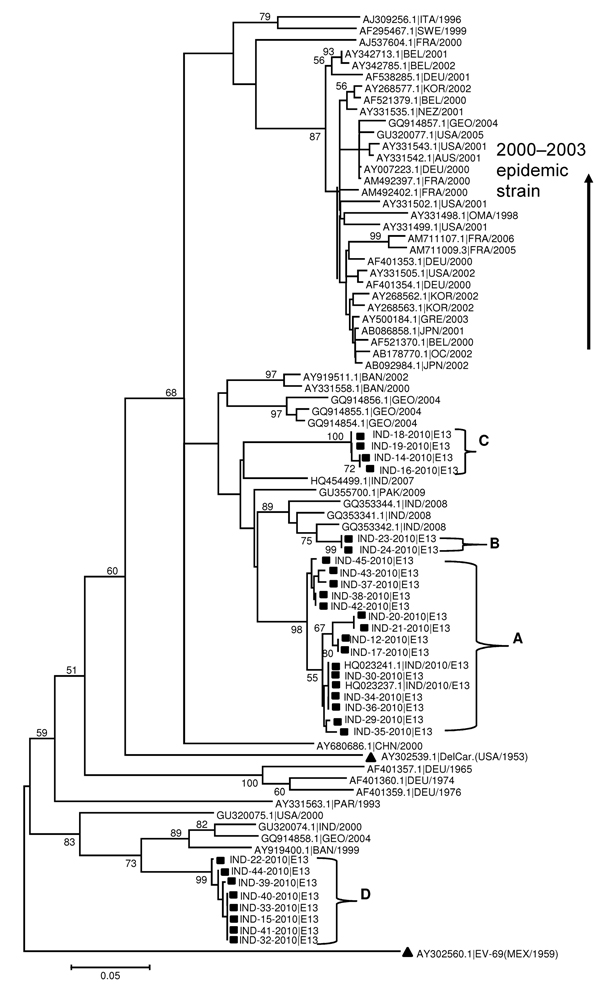
Figure. . Phylogenetic tree based on alignments of partial viral protein 1 gene sequences of echovirus 13 (E13) constructed by the neighbor-joining method implemented in MEGA version 5.05 software (7) by using the Kimura-2 parameter nucleotide substitution model. Bootstrap analysis included 1,000 pseudoreplicate datasets. Clusters are labeled A, B, C, and D. Square indicates Uttar Pradesh E13 from fecal samples. All Uttar Pradesh E13 isolates on the tree are identified by using the same numbers listed in Table 1. Triangle indicates E13 prototype Del Carmen and the out-group enterovirus 69. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Oberste MS, Maher K, Flemister MR, Marchetti G, Kilpatrick DR, Pallansch MA. Comparison of classic and molecular approaches for the identification of untypeable enteroviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:1170–4 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Oberste MS, Maher K, Kilpatrick DR, Pallansch MA. Molecular evolution of the human enteroviruses: correlation of serotype with VP1 sequence and application to picornavirus classification. J Virol. 1999;73:1941–8 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dhole TN, Ayyagari A, Chowdhary R, Shakya A, Shrivastav N, Datta T, Non-polio enteroviruses in acute flaccid paralysis children of India: vital assessment before polio eradication. J Paediatr Child Health. 2009;45:409–13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. Polio laboratory manual. 4th ed. Geneva: The Organization; 2004.
- Dias AP, Tavares FN, Costa EV, da Silva EE. Evaluation of a protocol for rapid diagnosis of enterovirus associated with acute flaccid paralysis cases. J Clin Virol. 2009;46:337–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Oberste MS, Nix WA, Maher K, Pallansch MA. Improved molecular identification of enteroviruses by RT-PCR and amplicon sequencing. J Clin Virol. 2003;26:375–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Junttila N, Leveque N, Kabue JP, Cartet G, Mushiya F, Muyembe-Tamfum JJ, New enteroviruses, EV-93 and EV-94, associated with acute flaccid paralysis in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. J Med Virol. 2007;79:393–400. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pérez-Vélez CM, Anderson MS, Robinson CC, McFarland EJ, Nix WA, Pallansch MA, Outbreak of neurologic enterovirus type 71 disease: a diagnostic challenge. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:950–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Khetsuriani N, Kutateladze T, Zangaladze E, Shutkova T, Penaranda S, Nix WA, High degree of genetic diversity of non-polio enteroviruses identified in Georgia by environmental and clinical surveillance, 2002–2005. J Med Microbiol. 2010;59:1340–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kumar A, Shukla D, Kumar R, Idris MZ, Misra UK, Dhole TN. An epidemic of encephalitis associated with human enterovirus B in Uttar Pradesh, India, 2008. J Clin Virol. 2011;51:142–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kumar A, Shukla D, Kumar R, Idris MZ, Jauhari P, Srivastava S, Molecular identification of enteroviruses associated with aseptic meningitis in children from India. Arch Virol. 2012; Epub ahead of print. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kobayashi K, Haruta T, Kubota M, Akiyoshi K, Suga T, Ito M. Clinical spectrum in hospitalized children with echovirus type 13 infection. Pediatr Int. 2005;47:185–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Apostol LN, Suzuki A, Bautista A, Galang H, Paladin FJ, Fuji N, Detection of non-polio enteroviruses from 17 years of virological surveillance of acute flaccid paralysis in the Philippines. J Med Virol. 2012;84:624–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mullins JA, Khetsuriani N, Nix WA, Oberste MS, LaMonte A, Kilpatrick DR, Emergence of echovirus type 13 as a prominent enterovirus. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:70–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: January 22, 2013
Page updated: January 22, 2013
Page reviewed: January 22, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.