Volume 19, Number 8—August 2013
Letter
Novel Norovirus GII.4 Variant, Shanghai, China, 2012
Figure
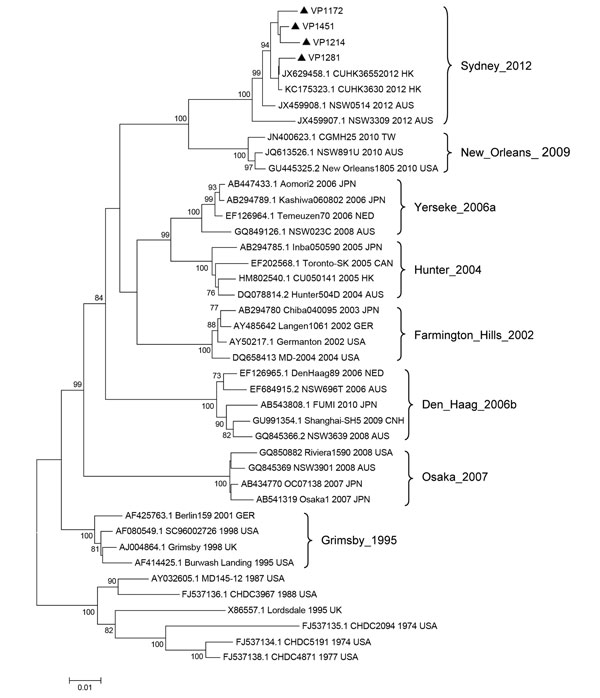
Figure. . . Phylogenetic tree of norovirus GII.4 capsid nucleotide sequences, Shanghai, China. The dendrogram was constructed by using the neighbor-joining method in MEGA version 5.0 (8). Bootstrap resampling (1,000 replications) was used, and bootstrap values ≥70% are shown. Black triangles indicate the 4 representative strains detected in Shanghai (GenBank accession nos. KC456070–KC456073). Reference sequences were obtained from GenBank and are indicated by GenBank accession number, strain name, year, and country of detection. Locations and years on the right indicate previously dominant GII.4 variants. HK, Hong Kong; AUS, Australia; TW, Taiwan; USA, United States; JPN, Japan; NED, the Netherlands; CAN, Canada; GER, Germany; CHN, China; UK, United Kingdom. Scale bar indicates distances between sequence pairs.