Volume 21, Number 2—February 2015
Research
Evidence for Elizabethkingia anophelis Transmission from Mother to Infant, Hong Kong
Figure 3
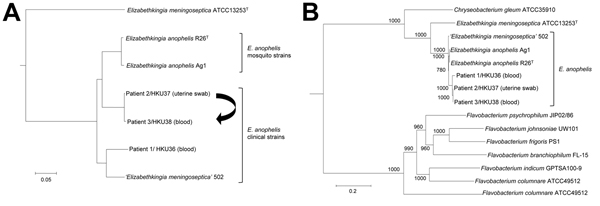
Figure 3. Phylogenetic trees constructed by using draft genome sequences and concatenated sequences of 69 housekeeping genes of 3 Elizabethkingia anophelis strains from patients in Hong Kong (HKU36–38). A) Neighbor-joining tree constructed on the basis of draft genome sequences using by using Genome-to-Genome Distance Calculator 2.0 (http://ggdc.dsmz.de/distcalc2.php; formula 1) and Chryseobacterium gleum ATCC 35910 as the root. Arrow indicates route of mother-to-neonate transmission. B) Maximum-likelihood tree constructed on the basis of 69 housekeeping genes, showing the relationship of E. anophelis strains HKU36–38 to related bacterial species, using RAxML version 7.2.8 (http://sco.h-its.org/exelixis/software.html) and Weeksella virosa DSM 16922 as the root. A total of 78,520 nt positions were included in the analysis. Bootstrap values were calculated from 1,000 replicates. Scale bars indicate mean number of nucleotide substitutions per site on the respective branches. Gene names and accession numbers are given as cited in GenBank (Technical Appendix Table 2). ‘E. meningoseptica’ strain 502 is a misidentified isolate that actually belongs to E. anophelis on the basis of draft genome sequencing.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.