Volume 21, Number 3—March 2015
Dispatch
Mycobacterium bovis Infection in Humans and Cats in Same Household, Texas, USA, 2012
Figure 1
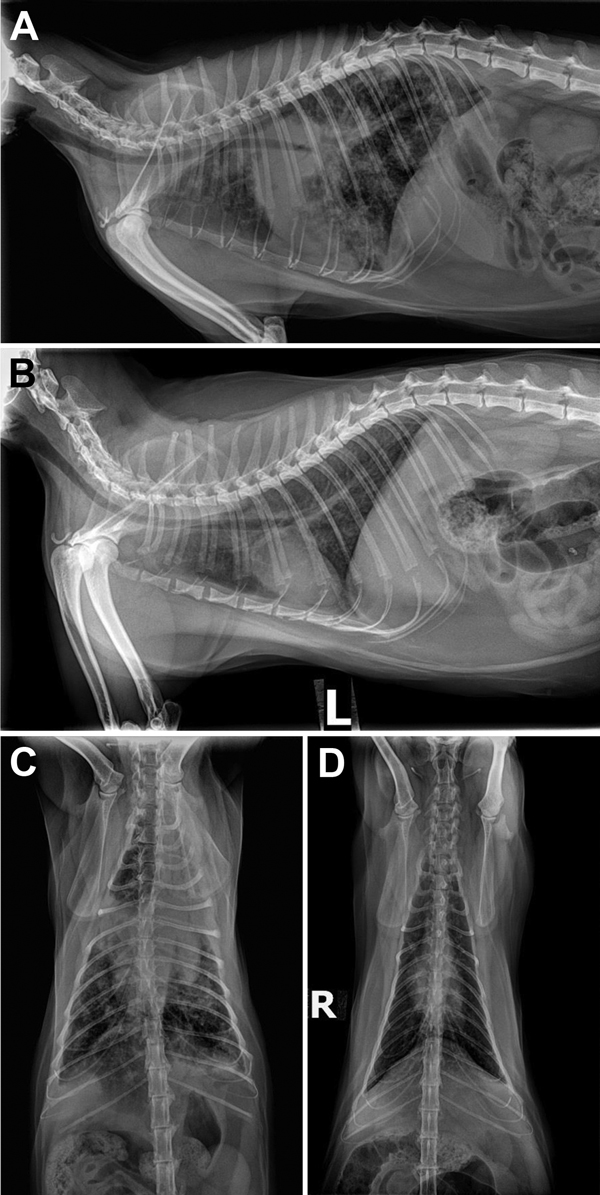
Figure 1. Radiograph images of cat Y showing pulmonary lesions before and after antimycobacterial treatment for Mycobacterium bovis infection, Texas, USA, 2012. A) Pretreatment, right lateral thoracic radiograph showing severe coalescing interstitial to alveolar pulmonary infiltrates before treatment. B) Posttreatment, left lateral thoracic radiograph after 2 months of marbofloxacin, rifampin, and a macrolide for 2 months in cat Y and then another 3.5 months of rifampin and marbofloxacin alone. C) Pretreatment, ventrodorsal view showing severe bronchointerstitial disease with poorly defined nodules or complete consolidation in the perihilar region, right middle lung lobe, and cranial segment of the left cranial lung lobe. D) Posttreatment, ventrodorsal thoracic radiographs after 2 months of triple antimycobacterial therapy and then another 3.5 months of rifampin and marbofloxacin alone. Considerable improvement occurred after therapy: the perihilar region cleared but a heavy interstitial marking throughout the lungs remained, most suggestive of fibrosis from scarring or, less likely, from smaller active granulomata.