Volume 21, Number 5—May 2015
Dispatch
Full-Genome Sequence of Influenza A(H5N8) Virus in Poultry Linked to Sequences of Strains from Asia, the Netherlands, 2014
Figure
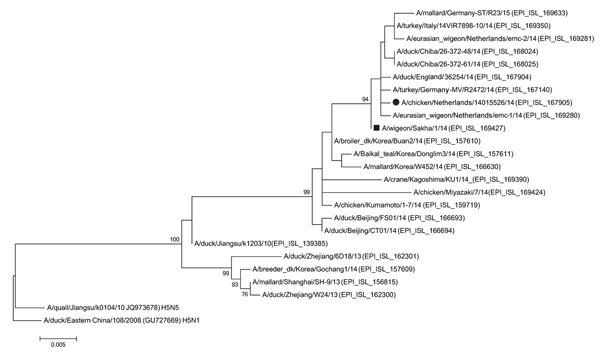
Figure. Phylogenetic tree of hemagglutinin gene of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N8) viruses. The evolutionary history was inferred by using the maximum-likelihood method based on the Tamura-Nei model in MEGA6 (14). The tree with the highest log likelihood is shown. The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches. Initial tree(s) for the heuristic search were obtained automatically by applying neighbor-joining and BIONJ (15) algorithms to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated by using the maximum composite likelihood approach and then selecting the topology with superior log likelihood value. The Tamura-Nei model was used by assuming a gamma distributed rate among nucleotide sites. The tree is drawn to scale; scale bar indicates the number of nucleotide substitutions per site. The analysis involved 25 nt sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 761 nt positions in the final dataset. Black dot indicates A/chicken/Netherlands/14015526/2014; black square indicates A/wigeon/Sakha/1/2014.
References
- Zhao K, Gu M, Zhong L, Duan Z, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Characterization of three H5N5 and one H5N8 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in China. Vet Microbiol. 2013;163:351–7 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee YJ, Kang HM, Lee EK, Song BM, Jeong J, Kwon YK, Novel reassortant influenza A(H5N8) viruses, South Korea, 2014. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:1087–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gu M, Zhao G, Zhao K, Zhong L, Huang J, Wan H, Novel variants of clade 2.3.4 highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) viruses, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:2021–4 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kang HM, Lee EK, Song BM, Jeong J, Choi JG, Jeong J, Novel reassortant influenza A(H5N8) viruses among inoculated domestic and wild ducks, South Korea, 2014. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:298–304 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jeong J, Kang HM, Lee EK, Song B-M, Kwon YK, Kim HR, Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (H5N8) in domestic poultry and its relationship with migratory birds in South Korea during 2014. Vet Microbiol. 2014;173:249–57. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- ProMED-Mail. Avian influenza (78): Avian influenza (52): Japan (KM) HPAI serotyped H5N8. 2014 Apr 17 [cited 2014 Nov 1]. http://www.promedmail.org, archive no. 20140417.2412249.
- Spackman E, Senne DA, Myers TJ, Bulaga LL, Garber LP, Perdue ML, Development of a real-time reverse transcriptase PCR assay for type A influenza virus and the avian H5 and H7 hemagglutinin subtypes. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:3256–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gall A, Hoffmann B, Harder T, Grund C, Beer M. Universal primer set for amplification and sequencing of HA0 cleavage sites of all influenza A viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:2561–7 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gall A, Hoffmann B, Harder T, Grund C, Ehricht R, Beer M. Rapid and highly sensitive neuraminidase subtyping of avian influenza viruses by use of a diagnostic DNA microarray. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2985–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jonges M, Welkers MR, Jeeninga RE, Meijer A, Schneeberger P, Fouchier RA, Emergence of the virulence-associated PB2 E627K substitution in a fatal human case of highly pathogenic avian influenza virus A(H7N7) infection as determined by Illumina ultra-deep sequencing. J Virol. 2014;88:1694–702. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 2012;9:357–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol. 2012;19:455–77. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:2725–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gascuel O. BIONJ: an improved version of the NJ algorithm based on a simple model of sequence data. Mol Biol Evol. 1997;14:685–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- ProMED-Mail. Avian influenza (116): Russia (SA) HPAI H5N8, wild bird, OIE. 2014 Dec 26 [cited 2015 Jan 15]. http://www.promedmail.org, archive no. 20141226.3056459.