Volume 21, Number 8—August 2015
Research
Prevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Pigs at the Time of Slaughter, United Kingdom, 2013
Figure
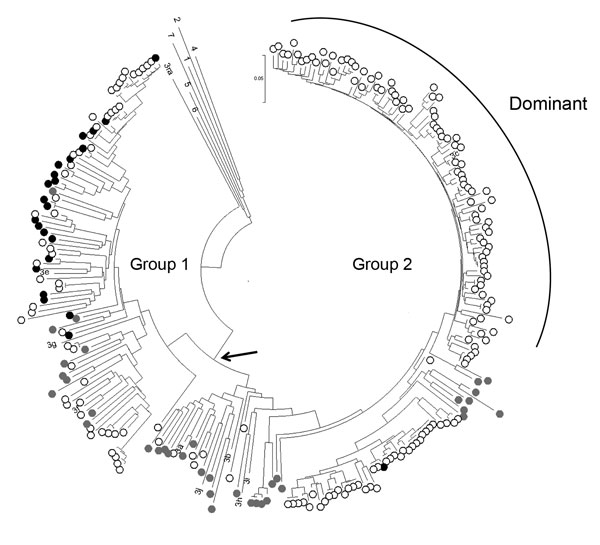
Figure. Phylogeny of genotype 3 hepatitis E viruses (HEVs) from pigs and patients with acute hepatitis in the United Kingdom. Nucleotide sequences of a 304-nt open reading frame 2 fragment (positions 5994–6297 of reference sequence M73218) from pigs at slaughter (black dots, n = 23) or from cases in persons with acute hepatitis E in England and Wales in 2013 (open circles, n = 190) were used to produce a neighbor-joining tree on the basis of maximum composite likelihood distances. GenBank accession numbers for porcine HEV sequences from this study are KP293752–774. Reference sequences were porcine sequences from Europe and North America from GenBank (gray dots, n = 36) and single examples of previously assigned HEV genotypes and subtypes for which complete genome sequences were available: 1, M73218; 2, M74506; 4, AJ272108; 5, AB573435; 6, AB602441; 7, KJ496143; 3a, AF082843; 3b, AB291955; 3c, FJ705359; 3e, AB248521; 3f, EU723514; 3g, AF455784; 3h, AB290312; 3i, FJ998008; 3j, AY115488; and 3ra, GU937805. Bootstrap support (500 replicates) for all major nodes, including those for genotypes 1–7, was weak (40%–70%), reflecting the short genome region and the large number of sequences analyzed. Arrow indicates the group 1/2 node.