Volume 22, Number 10—October 2016
Letter
Polymyxin B Resistance in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, São Paulo, Brazil
Figure
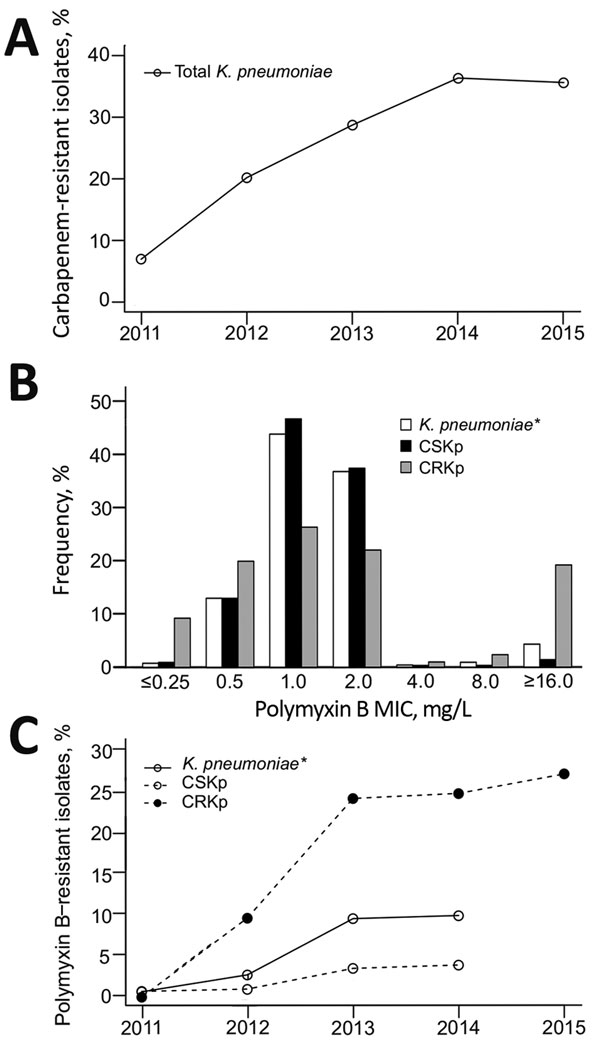
Figure. Antimicrobial resistance profile of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from hospital inpatients in São Paulo, Brazil. A) Carbapenem resistance trend among all K. pneumoniae isolates cultured during January 1, 2011–December 31, 2015 (n = 3,085; p<0.001). B) Polymyxin B MIC distribution stratified by carbapenem susceptibility. C) Polymyxin B resistance trend stratified by carbapenem susceptibility, 2011–2015. B, C) Carbapenem-susceptible K. pneumoniae (CSKp) isolated during January 1, 2011–June 30, 2014 (n = 1,511) and carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae (CRKp) isolated during January 1, 2011–December 31, 2014 (n = 436); *during July 1, 2015–December 31, 2015, only CRKp were tested for polymyxin B susceptibility (n = 377). All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS Studio 3.4 (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA). The statistical significance of a trend in resistance rates was evaluated using the χ2 test, in which p values <0.05 were considered significant: K. pneumoniae, p<0.001; CSKp, p = 0.004; CRKp, p = 0.003.