Volume 22, Number 11—November 2016
Research
Global Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131 Clade with blaCTX-M-27 Gene
Figure 1
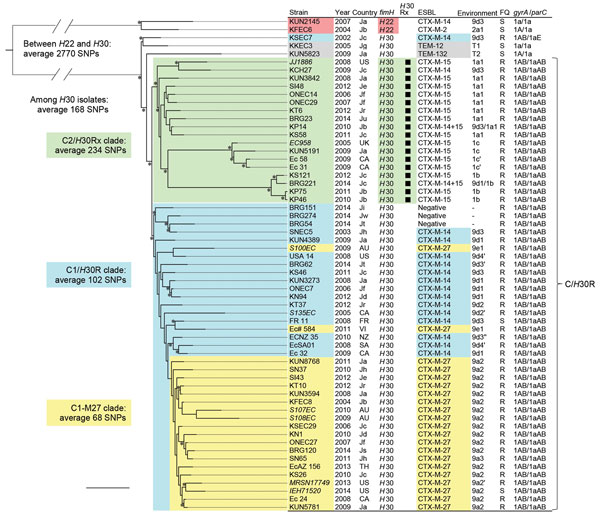
Figure 1. Core genome single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)–based phylogenetic tree of Escherichia coli sequence type (ST) 131 isolates. This maximum-likelihood phylogram is based on a 4,086,650-bp core genome and a total of 5,280 SNPs. The tree is rooted by using the outgroup H22 isolates, and asterisks indicate bootstrap support >90% from 100 replicates. Strains that had previously been sequenced are in bold. The Country columns indicate places of isolation: Ja to Jw, Japan (a to w indicates hospitals); AU, Australia; CA Canada; FR, France; NZ, New Zealand; SA, South Africa; TH, Thailand; UK, United Kingdom; US, United States; VI, Vietnam. Environment column shows a type of genetic environment of ESBL genes (Technical Appendix Table 2). FQ columns indicate ciprofloxacin susceptibilities (S, susceptible; R, resistant). KSEC7 had a parC 1aE allele including G250A (S80K) mutation in addition to a 1a allele. The ciprofloxacin-resistant C/H30R cluster comprised the C2/H30Rx and C1/H30R clades. All of the H30Rx isolates belonged to the C2/H30Rx clade. The C1/H30R clade included CTX-M-14–producing H30R, non–ESBL-producing H30R, and CTX-M-27–producing H30R isolates. CTX-M-27–producing isolates belonged to the C1-M27 clade within the C1/H30R clade except 2 isolates (S100EC and EC# 584). The bootstrap value for the root of the C1-M27 clade was 64%. An average of 68 SNPs was found among the C1-M27 clade, whereas an average of 158 SNPs was found between the C1-M27 clade and 2 non–C1-M27 clade isolates with blaCTX-M-27. Scale bar indicates 100 SNPs.