Uveitis and Systemic Inflammatory Markers in Convalescent Phase of Ebola Virus Disease
John R. Chancellor
1, Sriranjani P. Padmanabhan
1, Thomas C. Greenough, Richard Sacra, Richard T. Ellison, Lawrence C. Madoff, Rebecca J. Droms, David M. Hinkle, George K. Asdourian, Robert W. Finberg, Ute Stroher, Timothy M. Uyeki, and Olga M. Cerón

Author affiliations: University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts, USA (J.R. Chancellor, S.P. Padmanablan, T.C. Greenough, R. Sacra, R.T. Ellison III, L.C. Madoff, R.J. Droms, D.M. Hinkle, G.K. Asdourian, R.W. Finberg, O.M. Cerón); Massachusetts Department of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, USA (L.C. Madoff); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, USA (U. Stroher, T.M. Uyeki)
Main Article
Figure 2
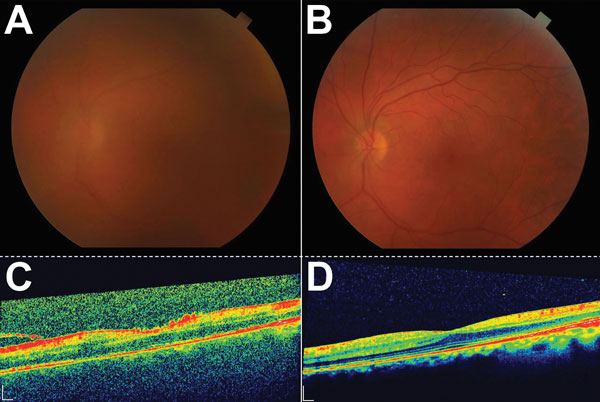
Figure 2. Color fundus and optical coherence tomography (OCT) images during active uveitis and after resolution for a physician from the United States who contracted Ebola virus disease in Liberia and had eye inflammation develop during convalescence. A) Color fundus image of the left eye showing a hazy view to the posterior pole during active uveitis (standardization of uveitis nomenclature classification grade 2–3). B) Color fundus image of the left eye showing a clear view to the posterior pole after resolution of uveitis. C) OCT of macula showing vitreous debris and small particles in a line of vitreous strands, consistent with inflammatory debris. D) OCT of macula showing resolution of vitreous and inflammatory debris. Scale bars indicate 200 μm.
Main Article
Page created: January 15, 2016
Page updated: January 15, 2016
Page reviewed: January 15, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
