Volume 22, Number 5—May 2016
Dispatch
Fatal Septicemia Linked to Transmission of MRSA Clonal Complex 398 in Hospital and Nursing Home, Denmark
Figure
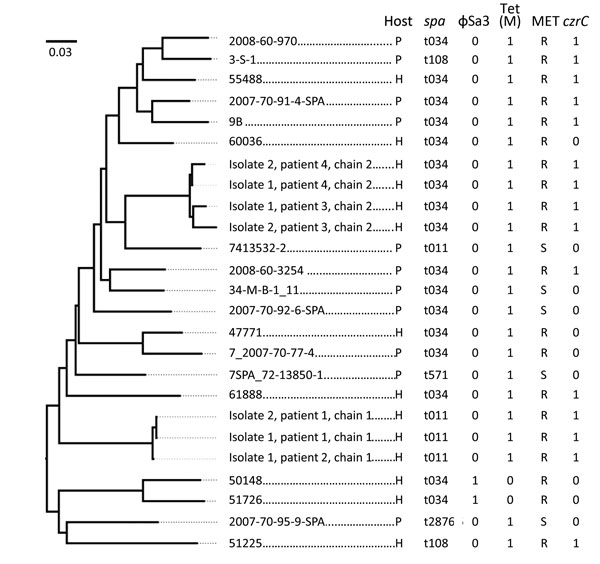
Figure. Phylogeny of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) clonal complex (CC) 398 isolates linked to fatal septicemia in a hospital patient and a nursing home resident in Denmark. Draft whole-genome sequencing was performed on 7 isolates from the 4 patients identified in the 2 transmission chains, and results were compared with similar genomic data for CC398-related MRSA and methicillin-sensitive S. aureus isolates obtained in Denmark during a previous study of isolates belonging to CC398 (13). Single-nucleotide polymorphism differences were identified, and a maximum-likelihood phylogeny was inferred from raw data by using the web tool CSI Phylogeny (https://cge.cbs.dtu.dk//services/CSIPhylogeny). The reference strain was S0385 (GenBank accession no. AM990992.1). The region of bp 12252–135180 was excluded from analysis because it contains the spa region and disrupts the phylogenic signal (13). Scale bar indicates substitutions per site. P, pig; H, human; MET, methicillin susceptibility; R, resistant; S, susceptible.