Volume 25, Number 8—August 2019
Dispatch
Kaposi Sarcoma in Mantled Guereza
Figure 2
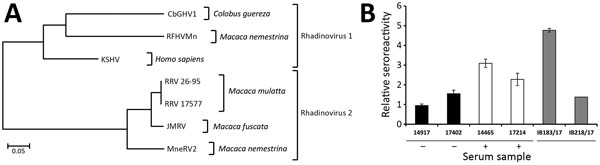
Figure 2. Analysis of CbGHV1 and seroreactivity in mantled guereza with Kaposi sarcoma. A) Phylogenetic analysis of partial sequences of the polymerase gene. Analysis was performed by using the neighbor-joining method. The distance between CbGHV1 and selected viruses was analyzed by using the maximum composite–likelihood method and MEGA6 (https://www.megasoftware.net). The PCR sequence of CbGHV1 was compared with KSHV (GenBank accession no. NC_009333.1); RFHVMn (KF703446.1); RRV 26–95 (AF210726.1); RRV 17577 (NC_003401.1); JMRV (AY528864.1); and MneRV2 (KP265674.2). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. B) Antibodies from mantled guereza with Kaposi sarcoma showing cross-reactivity against KSHV. Reactivities of KSHV antibody–positive human serum samples (14465 and 17214), KSHV antibody–negative human serum samples (14917 and 17402), and serum sample from the Kaposi sarcoma–affected mantled guereza (IB183/17) and its healthy offspring (IB218/17) were analyzed by ELISA. Relative reactivities of serum samples with KSHV-positive and KSHV-negative cell lysates are shown. The sum of relative errors is used as an error estimate for the ratio and is indicated by error bars (mean ± half error). Reactivity of human serum samples against KSHV is indicated. CbGHV1, Colobine gammaherpesvirus 1; JMRV, Japanese macaque rhadinovirus; KSHV, Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus; MneRV2, Macaca nemestrina rhadinovirus 2; RFHVMn, retroperitoneal fibromatosis–associated herpesvirus M. nemestrina; RRV, rhesus rhadinovirus; –, negative; +, positive.