Volume 19, Number 6—June 2013
Dispatch
BSE-associated Prion-Amyloid Cardiomyopathy in Primates
Abstract
Prion amyloidosis occurred in the heart of 1 of 3 macaques intraperitoneally inoculated with bovine spongiform encephalopathy prions. This macaque had a remarkably long duration of disease and signs of cardiac distress. Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, caused by transmission of bovine spongiform encephalopathy to humans, may manifest with cardiac symptoms from prion-amyloid cardiomyopathy.
Human prion diseases are progressive neurologic disorders that include sporadic, genetic, and acquired forms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) (1). A key step in disease initiation is conversion of PrPC into PrPSc, which is partially resistant to proteolytic digestion and an essential part of prion infectivity. Transmission of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) to humans has led to a novel form of acquired CJD, termed variant CJD (vCJD) (2). The pathogenesis of vCJD differs substantially from sporadic CJD with remarkable colonization of non–central nervous system regions with infectious prions and PrPSc (3).
Although risk reduction measures have been introduced to limit transmission from BSE-diseased cattle to humans, vCJD has occurred in several hundred instances (www.eurocjd.ed.ac.uk). Most clinically affected vCJD patients are homozygous for methionine on polymorphic codon 129 on the gene coding PrP (PRNP), and the clinical presentation of vCJD in these patients is uniform (4). The occurrence of atypical clinical features in persons with vCJD that encodes methionine and valine on PRNP codon 129 and human-to-human transmission of vCJD through blood transfusion have raised concern about atypical clinical features and alternative distribution of PrPSc in vCJD (5). We report on the novel clinicopathologic characteristics of vCJD as prion-amyloid cardiomyopathy in 1 of 3 macaques inoculated with BSE.
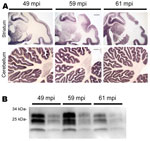
In 2002, three rhesus macaques were inoculated with BSE intraperitoneally (10 mL of a 10% homogenate of brain from BSE-diseased cattle). As controls, 2 rhesus macaques received saline (10 mL) and 1 was untreated. All procedures involving rhesus macaques were performed at the Institute of Neuropathology, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Hamburg, Germany), in accordance with the German Animal Welfare Act and the Council Directive 86/609/EEC (Permit 33.42502/08–08.02 LAVES, Lower Saxony, Germany). Animals were observed for clinical signs of prion disease and, when signs of terminal prion disease became evident, were euthanized and underwent autopsy. In all 3 BSE-challenged macaques and none of the controls a progressive neurologic disease developed 49, 59, and 61 months postinoculation. Examination of brain by using hematoxylin and eosin staining showed typical neuropathologic features of vCJD (data not shown) and abundant deposits of PrPSc in the cortex, basal ganglia, and cerebellum in paraffin-embedded tissue blots performed as described by using 12F10 monclonal antiprion antibody (6) (Figure 1, panel A). The mobility of the unglycosylated PrPSc band and the glycoform ratio of proteinase K–digested PrPSc were similar to those in BSE when assessed by Western blot analysis by using monoclonal POM-1 antiprion antibody as described (7) (Figure 1, panel B).
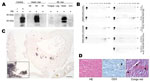
Besides lymphoreticular tissues, the muscular compartment is targeted by prions (7,8). Thus, we assessed presence of PrPSc in skeletal and heart muscle by Western blot analysis with sodium phosphotungstic acid precipitation for enrichment of PrPSc and protein misfolding cyclic amplification by using published protocols (3). We could not detect substantial amounts of PrPSc in skeletal muscle (Figure 2, panel A). One macaque showed abundant PrPSc (≈1/100 of PrPSc found in brain) in heart in Western blot and protein misfolding cyclic amplification (Figure 2, panels A, B). Paraffin-embedded tissue blot analysis of this heart showed PrPSc as amyloid, occupying considerable stretches of heart tissue, mainly in the septum (Figure 2, panel C), whereas no PrPSc could be seen in hearts of other macaques (data not shown). These findings were confirmed by strong Congo red–positive patch-like depositions in cardiomyocytes in the heart of this monkey (Figure 2, panel D). The primate with cardiac PrPSc showed the longest disease duration (4 months, compared with 4 weeks for other BSE-infected monkeys), signs of cardiac affection when assessed by relevant makers of cardiac hypertrophy and of cardiac distress–associated inflammation, and only this macaque showed clinical signs of fatigue and signs of cardiac distress (i.e., venous congestion) on autopsy (Technical Appendix, Table). Histologic examination of heart tissue with hematoxylin and eosin staining and immunohistochemical stainings against B and T cells (CD20 [not shown] and CD3) did not provide evidence for toxic cardiomyopathy (i.e., fibrosis or vacuolization), nor did we find signs of inflammatory reaction (Figure 2, panel D).
Although the vCJD epidemic is declining, considerable concern exists that clinical characterastics of vCJD will shift. The most important genetic risk factor for development of vCJD is homozygosity for methionine on PRNP codon 129, and all but 1 patient with clinical vCJD carry this polymorphism (5). Thus, future cases of vCJD with longer incubation times are likely to comprise more patients with alternative codon 129 polymorphisms than methionine homozygosity. Data from rodent experiments indicate that clinical features of vCJD may differ in these patients (9). Thus, the next decades may see a shift in vCJD phenotypes. Further uncertainty for atypical cases in humans results from the possibility of secondary transmission of vCJD through blood products from subclinical carriers, which may lead to development of nonclassical vCJD phenotypes (5).
We showed that BSE infection of primates may occur as prion-amyloid cardiomyopathy. Because prion-amyloid cardiomyopathy developed in only 1 of 3 macaques, host-encoded factors, such as genetic makeup, probably influence development of this cardiac phenotype. All macaques are homozygous for methionine on PRNP codon 129; thus, prion-amyloid cardiomyopathy cannot be related to polymorphic codon 129 in our study (10). Cardiac involvement has been observed in a patient with sporadic CJD and is prominent in prion-diseased mice expressing PrPC lacking its membrane anchor (11,12). We considered the possibility that preexisting pathology, such as spontaneous cardiomyopathy or inflammation of the heart, might have contributed to cardiac PrPSc, and the fact that we did not find any evidence for toxic cardiomyopathy or inflammation in the primate does not exclude this possibility. Because the macaque with abundant PrPSc deposition in heart had longer disease duration, it is also possible that longer disease duration, which favors centrifugal spread of prions to peripheral tissues, contributed to cardiac affection in this primate (7). Peripheral deposition of PrPSc in vCJD is well studied (3). We were surprised by the amount and deposition type of PrPSc in heart, reaching 1/100 of the amount seen in brain and deposited as amyloid across large stretches of heart tissue. Skeletal muscle of prion-diseased patients and nonhuman primates routinely harbor minimal amounts of PrPSc (<1/1000 that found in brain), and PrPSc in muscle is virtually impossible to detect by in situ methods (6,8,13). To our knowledge, PrPSc has not been detected in heart of vCJD-diseased persons or in patients with systemic amyloidosis, although primates orally exposed to BSE show very low amounts of cardiac PrPSc (8,14,15). The lack of cardiac PrPSc in vCJD may result from small cohorts investigated. Because the spectrum of vCJD is likely to change, broad application of current clinical criteria for vCJD in clinical practice may lead to underreporting of vCJD, missing atypical cases of vCJD.
In conclusion, we showed that BSE-infection of primates may lead to prion-amyloid cardiomyopathy. These data should be considered when vCJD surveillance is conducted.
Dr Krasemann is a research scientist at the Institute of Neuropathology of the University of Hamburg working on prion spread. Her primary research interests are factors involved in spread and clearance of prions.
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by the European Union grant EU BMH4 CT 98 7026, DFG grants KA 864/2-1, GL 589/2-1, and the BMBF-DLR grant 01GZ0712 to S.K.
The overall study was conceived and designed by M.G., A.A., F.J.K., and S.K. Animal care, housing, and observation were conducted by F.J.K., W.B., and W.S.S. Experiments were performed by S.K., G.M., E.K., K.W., W.S.S., and M.N. Data were analyzed by S.K., G.M., M.B., A.A., and M.G. S.K. and M.G. wrote the paper with substantial contributions from G.M. and A.A.
References
- Geissen M, Krasemann S, Matschke J, Glatzel M. Understanding the natural variability of prion diseases. Vaccine. 2007;25:5631–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Will RG, Ironside JW, Zeidler M, Cousens SN, Estibeiro K, Alperovitch A, A new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the UK. Lancet. 1996;347:921–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wadsworth JDF, Joiner S, Hill AF, Campbell TA, Desbruslais M, Luthert PJ, Tissue distribution of protease resistant prion protein in variant CJD using a highly sensitive immuno-blotting assay. Lancet. 2001;358:171–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Heath CA, Cooper SA, Murray K, Lowman A, Henry C, MacLeod MA, Validation of diagnostic criteria for variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol. 2010;67:761–70 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kaski D, Mead S, Hyare H, Cooper S, Jampana R, Overell J, Variant CJD in an individual heterozygous for PRNP codon 129. Lancet. 2009;374:2128. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Krasemann S, Neumann M, Geissen M, Bodemer W, Kaup FJ, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Preclinical deposition of pathological prion protein in muscle of experimentally infected primates. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e13906. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Glatzel M, Abela E, Maissen M, Aguzzi A. Extraneural pathologic prion protein in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1812–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Peden AH, Ritchie DL, Head MW, Ironside JW. Detection and localization of PrPSc in the skeletal muscle of patients with variant, iatrogenic, and sporadic forms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Am J Pathol. 2006;168:927–35. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Asante EA, Linehan JM, Gowland I, Joiner S, Fox K, Cooper S, Dissociation of pathological and molecular phenotype of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in transgenic human prion protein 129 heterozygous mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:10759–64. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Glatzel M, Pekarik V, Luhrs T, Dittami J, Aguzzi A. Analysis of the prion protein in primates reveals a new polymorphism in codon 226 (Y226F). Biol Chem. 2002;383:1021–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Trifilo MJ, Yajima T, Gu Y, Dalton N, Peterson KL, Race RE, Prion-induced amyloid heart disease with high blood infectivity in transgenic mice. Science. 2006;313:94–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ashwath ML, Dearmond SJ, Culclasure T. Prion-associated dilated cardiomyopathy. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:338–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Herzog C, Sales N, Etchegaray N, Charbonnier A, Freire S, Dormont D, Tissue distribution of bovine spongiform encephalopathy agent in primates after intravenous or oral infection. Lancet. 2004;363:422–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tennent GA, Head MW, Bishop M, Hawkins PN, Will RG, Knight R, Disease-associated prion protein is not detectable in human systemic amyloid deposits. J Pathol. 2007;213:376–83. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Herzog C, Riviere J, Lescoutra-Etchegaray N, Charbonnier A, Leblanc V, Sales N, PrPTSE distribution in a primate model of variant, sporadic, and iatrogenic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Virol. 2005;79:14339–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Figures
Table
Cite This Article1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Table of Contents – Volume 19, Number 6—June 2013
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Markus Glatzel, Institute of Neuropathology, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Martinistrasse 52, D-20246 Hamburg, Germany
Top