Volume 11, Number 10—October 2005
Dispatch
Genetic Characterization of Nipah Virus, Bangladesh, 2004
Figure
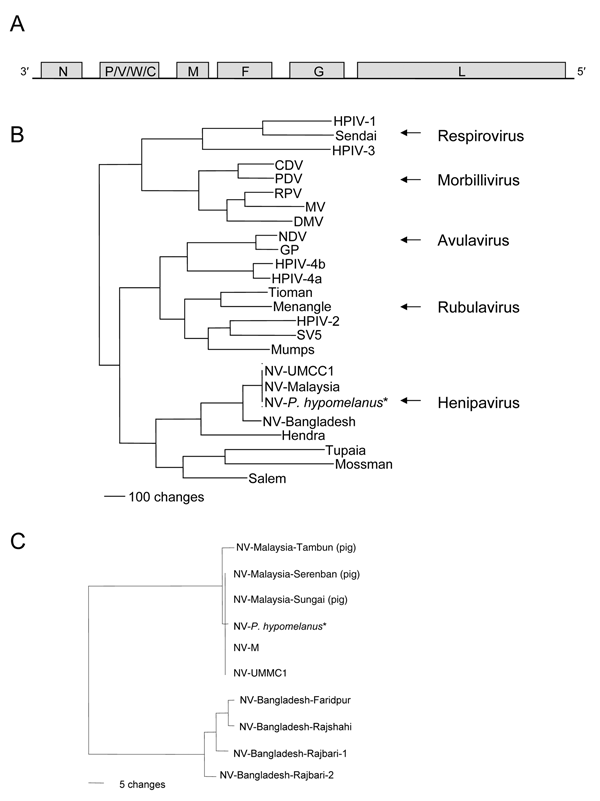
Figure. A) Schematic representation of the genome of Nipah virus (NV). Negative-sense genomic RNA is shown in 3´ to 5´ orientation. Open reading frames (ORFs) are indicated by shaded boxes: N, nucleoprotein; P, phosphoprotein; M, matrix protein; F, fusion protein; G, attachment protein; L, polymerase protein. B) Phylogenetic analysis of the N ORFs from members of the subfamily Paramyxovirinae. Arrows identify the 5 genera. A phenogram of the N ORFs of members of this subfamily was created by using maximum parsimony analysis with PAUP 4.02 (Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, USA). Abbreviations and accession numbers: HPIV-1, human parainfluenza virus, D01070; Sendai, X00087; HPIV-3, D10025; CDV, canine distemper virus, AF014953; PDV, phocine distemper virus, X75717; RPV, Rinderpest virus, X68311; MV, K01711; DMV, dolphin Morbillivirus, X75961; NDV, Newcastle disease virus, AF064091; GP, goose paramyxovirus, AF473851; HPIV-4b, M32983; HPIV-4a, M32982; Tioman, AF298895; Menangle, AF326114; HPIV-2, M55320; Simian virus 5 (SV5), M81442; Mumps, D86172; NV-UMCC1, AY029767; NV-Malaysia, AF212302; NV-P. hypomelanus,* AF376747; NV-Bangladesh; Hendra virus, AF017149; Tupaia paramyxovirus, AF079780; Mossman virus, AY286409; and Salem virus, AF237881. C) The phylogenetic relationship between the N gene sequences of the 4 human NV isolates from the Bangladesh outbreak in 2004 and the N gene sequences from pig and human NV isolates from Malaysia. Accession numbers for the pig isolates of NV (13) are AJ627196, AJ564622, and AJ564621. *NV-P. hypomelanus is sequence from a virus isolated from Pteropus hypomelanus, the Island Flying Fox (8).
References
- Chua KB, Bellini WJ, Rota PA, Harcourt BH, Tamin A, Lam SK, Nipah virus: a recently emergent deadly paramyxovirus. Science. 2000;288:1432–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Harcourt BH, Tamin A, Ksiazek TG, Rollin PE, Anderson LJ, Bellini WJ, Molecular characterization of Nipah virus, a newly emergent paramyxovirus. Virology. 2000;271:334–49. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Harcourt BH, Tamin A, Halpin K, Ksiazek TG, Rollin PE, Bellini WJ, Molecular characterization of the polymerase gene and genomic termini of Nipah virus. Virology. 2001;287:192–201. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang LF, Harcourt BH, Yu M, Tamin A, Rota PA, Bellini WJ, Molecular biology of Hendra and Nipah viruses. Microbes Infect. 2001;3:279–87. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chua KB, Lam SK, Goh KJ, Hooi PS, Ksiazek TG, Kamarulzaman A, The presence of Nipah virus in respiratory secretions and urine of patients during an outbreak of Nipah virus encephalitis in Malaysia. J Infect. 2001;42:40–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mounts AW, Kaur H, Parashar UD, Ksiazek TG, Cannon D, Arokiasamy JT, ; Nipah Virus Nosocomial Study Group. A cohort study of health care workers to assess nosocomial transmissibility of Nipah virus. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:810–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yob JM, Field H, Rashdi AM, Morrissy C, van der Heide B, Rota P, Nipah virus infection in bats (order Chiroptera) in peninsular Malaysia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001;7:439–41.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chua KB, Koh CL, Hooi PS, Wee KF, Khong JH, Chua BH, Isolation of Nipah virus from Malaysian island flying-foxes. Microbes Infect. 2002;4:145–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- ICDDRB. Nipah encephalitis outbreak over wide area of western Bangladesh. Health Science Bulletin. 2004;2:7–11.
- ICDDRB. Person-to-person transmission of Nipah virus during outbreak in Faridpur District. Health Science Bulletin. 2004;2:5–9.
- World Health Organization. Nipah virus outbreak(s) in Bangladesh, January–April 2004. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2004;79:168–71.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hsu VP, Hossain MJ, Parashar UD, Ali MM, Ksiazek TG, Kuzmin I, Nipah virus encephalitis reemergence, Bangladesh. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:2082–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- AbuBakar S, Chang LY, Ali AR, Sharifah SH, Yusoff K, Zamrod Z. Isolation and molecular identification of Nipah virus from pigs. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:2228–30.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rodriguez JJ, Cruz CD, Horvath CM. Identification of the nuclear export signal and STAT-binding domains of the Nipah virus V protein reveals mechanisms underlying interferon evasion. J Virol. 2004;78:5358–67. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Poch O, Blumberg BM, Bougueleret L, Tordo N. Sequence comparison of five polymerases (L proteins) of unsegmented negative-strand RNA viruses: theoretical assignment of functional domains. J Gen Virol. 1990;71:1153–62. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reynes JM, Counor D, Ong S, Faure C, Seng V, Molia S, Nipah virus in Lyle's Flying Foxes, Cambodia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:1042–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar