Volume 11, Number 7—July 2005
Dispatch
Cervids as Babesiae Hosts, Slovenia
Figure
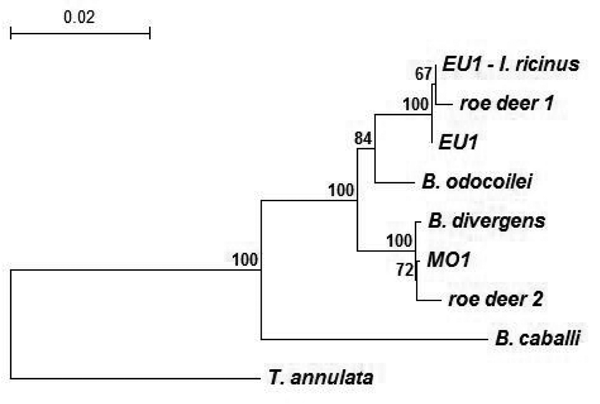
Figure. . Phylogenetic relationships of representative babesiae deposited in GenBank and detected in this study, inferred from multiple sequence alignment of complete 18S rRNA gene. Accession numbers of babesiae: Babesia EU1 from Ixodes ricinus ticks, AY553915; babesiae from roe deer 1, AY572457; babesiae from roe deer 2, AY572456; Babesia EU1 from human, AY046575; B. divergens, AY046576; B. odocoilei, AY046577; Babesia MO1, AY048113; B. caballi, Z15104; and Theileria annulata, M64243. The number on each branch shows the percent occurrence in 1,000 bootstrap replicates.
Page created: April 23, 2012
Page updated: April 23, 2012
Page reviewed: April 23, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.