Volume 12, Number 3—March 2006
Dispatch
West Nile Virus–associated Flaccid Paralysis Outcome
Figure A1
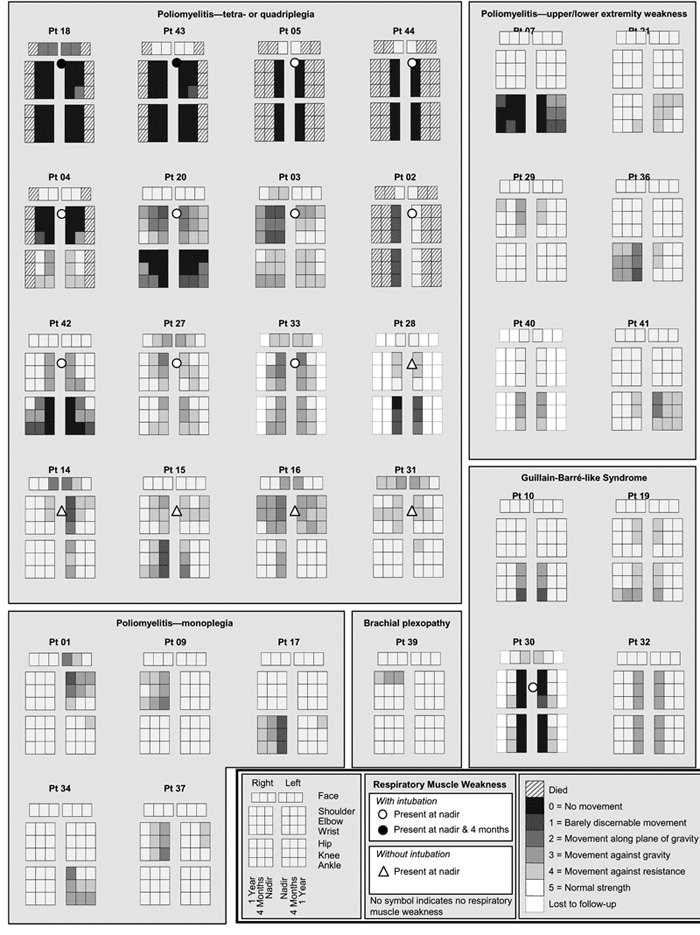
Figure A1. Patterns of weakness at strength nadir, 4 months, and 1 year in patients with acute paralysis and West Nile virus infection. Shadings indicate strength scoring on manual muscle testing and represent the average strength score of all tested muscles proximally (upper extremity: shoulder adduction/abduction, arm internal/external rotation; lower extremity: hip flexion/extension, thigh adduction/abduction), medially (upper extremity: elbow flexion/extension, pronation/supination; lower extremity: knee flexion/extension), and distally (upper extremity: wrist flexion/extension, finger flexion/extension; lower extremity: ankle plantarflexion/dorsiflexion, foot inversion/eversion, toe flexion/extension) in each limb and the facial muscles; scores were rounded down to the lowest whole number. Patients with respiratory weakness are indicated by circles (intubated) or triangles (not intubated). All patients surviving to 1 year were successfully extubated.