Volume 12, Number 3—March 2006
Dispatch
Canine Coronavirus Highly Pathogenic for Dogs
Figure 2
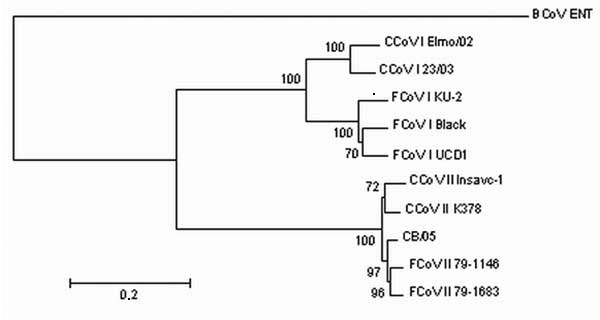
Figure 2. Neighbor-joining tree of the spike protein of canine coronavirus (CCoV) and feline coronavirus (FCoV). The following reference strains were used for phylogenetic analysis: CCoV type I strains Elmo/02 (GenBank accession no. AY307020) and 23/03 (AY307021); CCoV type II strains Insavc-1 (D13096) and K378 (X77047); FCoV type I strains KU-2 (D32044), Black (AB088223) and UCD-1 (AB088222); FCoV type II strains 79-1146 (X06170) and 79-1683 (X80799); and bovine coronavirus (BCoV) strain ENT (NC_003045). The tree is rooted on BCoV-ENT and drawn to scale. A statistical support was provided by bootstrapping >100 replicates. The scale bar represents 20 substitutions per 100 sequence positions.feline coronavirus (FCoV). The following reference strains were used for phylogenetic analysis: CCoV type I strains Elmo/02 (GenBank accession no. AY307020) and 23/03 (AY307021); CCoV type II strains Insavc-1 (D13096) and K378 (X77047); FCoV type I strains KU-2 (D32044), Black (AB088223) and UCD-1 (AB088222); FCoV type II strains 79-1146 (X06170) and 79-1683 (X80799); and bovine coronavirus (BCoV) strain ENT (NC_003045). The tree is rooted on BCoV-ENT and drawn to scale. A statistical support was provided by bootstrapping >100 replicates. The scale bar represents 20 substitutions per 100 sequence positions.