Volume 16, Number 12—December 2010
Dispatch
Alkhurma Hemorrhagic Fever in Travelers Returning from Egypt, 2010
Figure 2
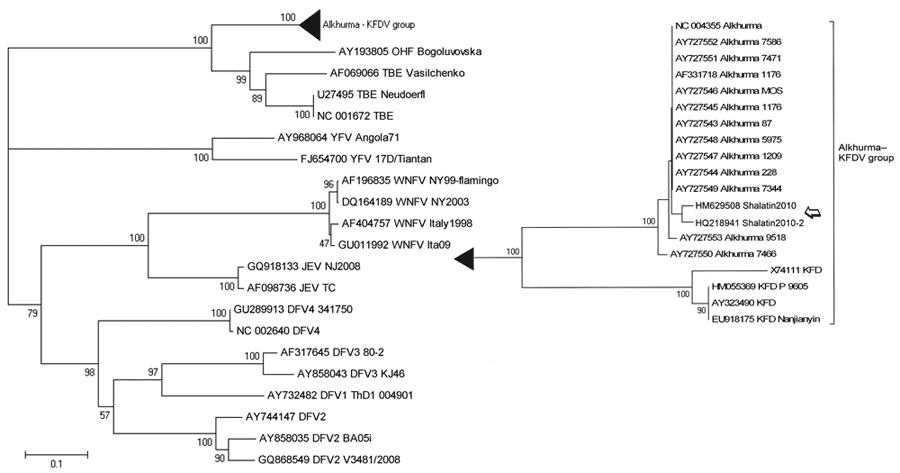
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree based on the sequences of Alkhurma hemorrhagic fever virus E gene amplicon (amplicon size, 516 bp; position in reference AF331718, nt 1398–1913),obtained from acute-phase serum samples from a patient who had traveled to Egypt (open arrow) with respect to other flaviviruses. Sequences are identified by name and GenBank accession number. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by nucleotide alignment, the Kimura 2-parameter algorithm, and the neighbor-joining method implemented in MEGA 4.1 software (www.megasoftware.net). The robustness of branching patterns was tested by 1,000 bootstrap pseudo-replications. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. DFV, dengue fever virus; JEV, Japanese encephalitis virus; WNFV, West Nile fever virus; TBEV, tick-borne encephalitis virus; OHFV, Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus; KFDV, Kyasanur Forest disease virus. The relevant part of the tree is enlarged at right.