Volume 17, Number 1—January 2011
Letter
Ceftriaxone-Resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Japan
Figure
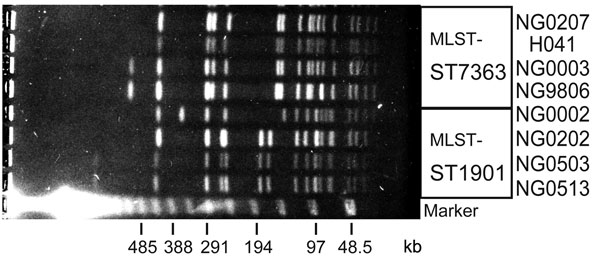
Figure. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis patterns of ceftriaxone-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain H041 and other multilocus sequence typing (MLST) ST7363 and ST1901 strains. SpeI-digested genomic DNA from ceftriaxone-resistant N. gonorrhoeae H041, 3 of the MLST ST7363 strains and 4 of the MLST ST1901 strains were analyzed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. A lambda ladder standard (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) was used as a molecular size marker.
Page created: July 08, 2011
Page updated: July 08, 2011
Page reviewed: July 08, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.