Volume 17, Number 8—August 2011
Dispatch
Pygmy Rice Rat as Potential Host of Castelo dos Sonhos Hantavirus
Figure 1
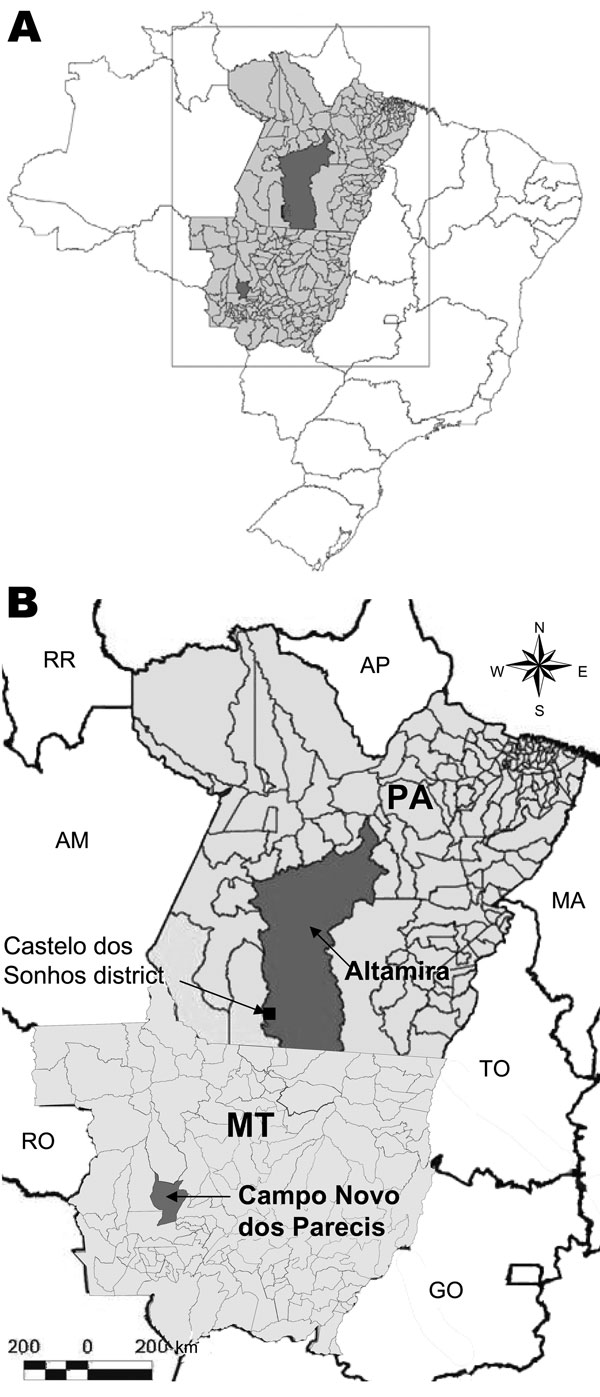
Figure 1. Location of Mato Grosso State, Brazil, showing the municipality of Campo Novo do Parecis where pygmy rice rats (Oligoryzomys utiaritensis) were found infected with Castelo dos Sonhos virus and the Castelo dos Sonhos district in the municipality of Altamira, Pará State, both locations where hantavirus pulmonary syndrome cases caused by Castelo dos Sonhos virus have been frequently found. MT, Mato Grosso State; PA, Pará State; AP, Amapá State; AM, Amazonas State; MA, Maranhão State; TO, Tocantins State; RO, Rondônia State; GO, Goiás State. Source: Laboratório de Geoprocessamento do Instituto Evandro Chagas, Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde do Ministério da Saúde.
Page created: August 15, 2011
Page updated: August 15, 2011
Page reviewed: August 15, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.