Volume 17, Number 8—August 2011
Dispatch
Pygmy Rice Rat as Potential Host of Castelo dos Sonhos Hantavirus
Figure 2
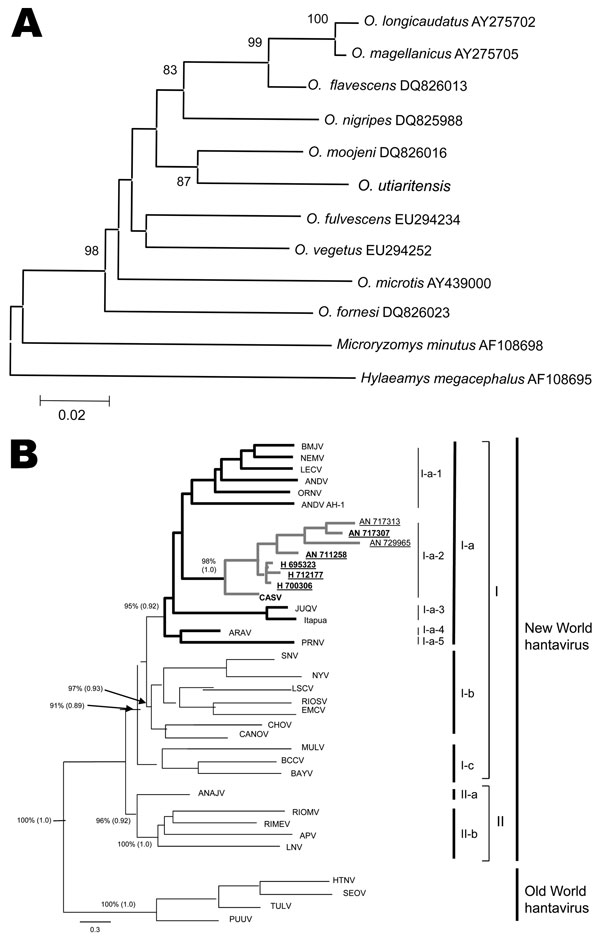
Figure 2. A) Phylogenetic tree constructed by using the neighbor-joining method for characterization of pygmy rice rats by using the cytochrome b DNA. Scale bar indicates nucleotide sequence divergence among the rodent species sequences. B) Phylogenetic tree using the maximum-likelihood (ML) and Bayesian methods based on partial nucleotide sequences of N gene obtained from pygmy rice rats captured in Campo Novo do Parecis, Mato Grosso State, Brazilian Amazon (New World major group, Group I, Clade Ia, Subclade Ia2, underlined strains and branches highlighted in boldface). Numbers at right indicate (left to right) subclades, clades, groups, and major groups. Green branch corresponds to Castelo dos Sonhos virus, including prototype strain, samples from pygmy rice rats, and hantavirus pulmonary syndrome–associated strains. Values over each main node placed outside and inside parentheses correspond to ML (bootstrap values) and Bayesian posterior probabilities (BPP), respectively. The arrows indicate the exact position for the bootstrap and BPP values over the main branch nodes. Scale bar indicates nucleotide sequence divergence among the hantavirus sequences. APV, Alto Paraguay virus (DQ345762); ANAJV, Anajatuba virus (DQ451829); ANDV, Andes virus (AF291702); Andes AH-1, Andes virus strain AH-1 (AF324902); ARAV: Araraquara virus (AF307325); BAYV: Bayou virus (L36929); BMJV, Bermejo virus (AF482713); BCCV, Black Creek Canal virus (L39949); CANOV, Caño Delgatito virus (DQ285566); CASV, Castelo dos Sonhos virus (AF307324); CHOV, Choclo virus (DQ285046); EMCV, El Moro Canyon virus (U54577); HTNV, Hantaan virus (NC005218); JUQV, Juquitiba virus (EF492472); LNV, Laguna Negra virus (AF005727); LECV, Lechiguanas virus (AF482714); LSCV, Limestone Canyon virus (AF307322); MULV, Muleshoe virus (U54576); NYV, New York virus (U09488); ORNV, Oran virus (AF482715); PRNV, Pergamino virus (AF482717); PUUV, Puumala virus (NC005224); RIOMV, Rio Mamore virus (U52138); RIMEV, Rio Mearim virus (DQ451828); RIOSV, Rio Segundo virus (U18100); SEOV, Seoul virus (NC005236); SNV, Sin Nombre virus (NC_005216); TULV, Tula virus (NC005227). H 695323 (HQ719468), H 712177 (HQ719467) and H 700306 (HQ719466) represent human CASV sequences obtained from patients with hantavirus pulmonary syndrome residing near the area where CASV has been recovered from pygmy rice rats.