Volume 18, Number 5—May 2012
Dispatch
Novel Human Adenovirus Strain, Bangladesh
Figure A1
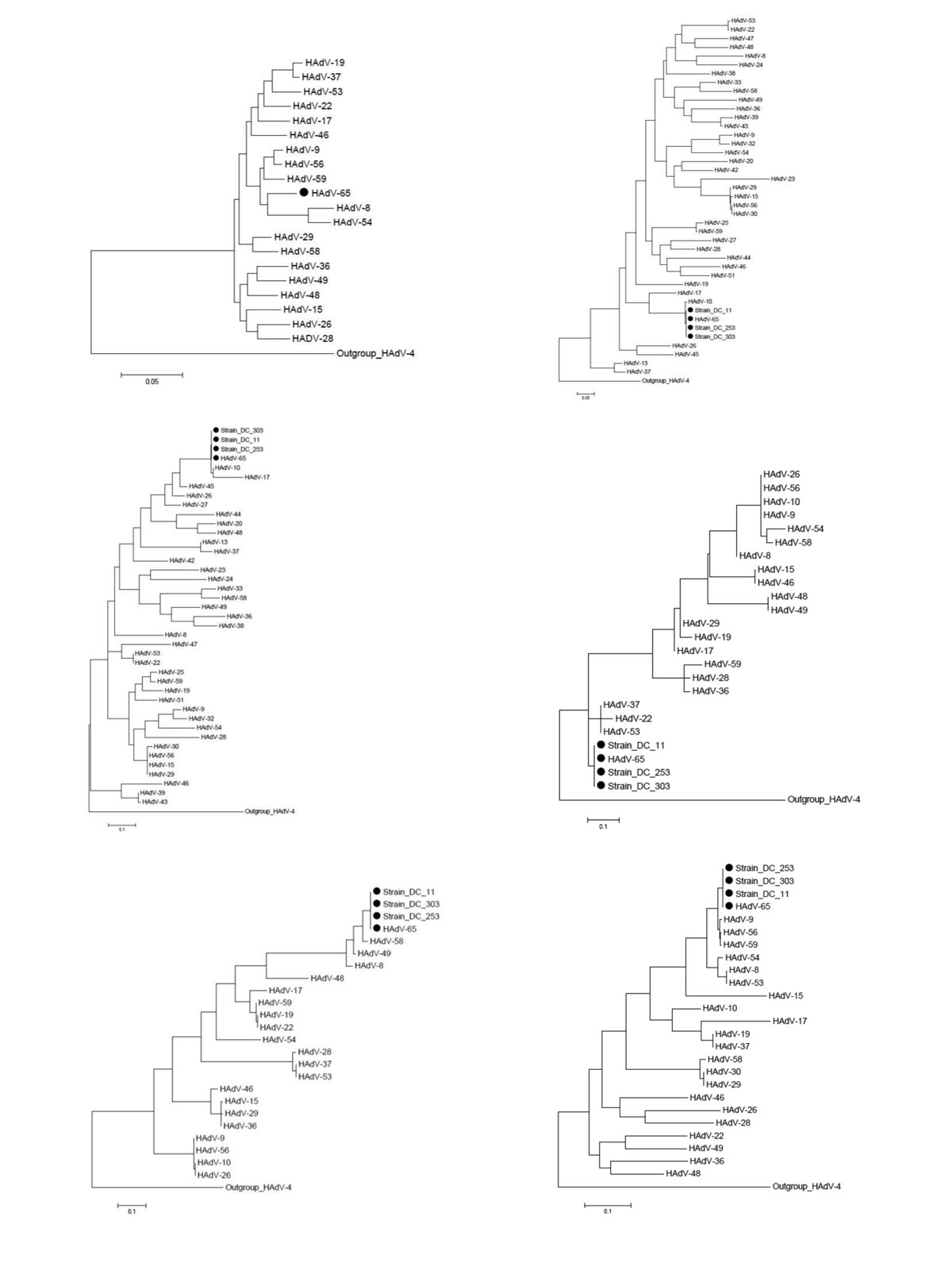
Figure A1. . Phylogenetic trees of a novel human adenovirus (HAdV-65), 3 strains (DC 11, DC 253, and DC 303), and other HAdV-D reference strains. Full genome sequences (except for the 3 strains) (A), loop 1 (B) and loop 2 (C) sequences of hexon gene, hypervariable loop 1 of penton base gene (D), Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) loop of penton base gene (E), and fiber gene (F). Black dots indicate new strains isolated in this study. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site. Adenoviruses HAdV-8 (DQ149614, AB448767), HAdV-9 (AJ854486), HAdV-10 (DQ149615, DQ375463, AB369368), HAdV-13 (DQ149616), HAdV-15 (DQ149617, AB562586), HAdV-17 (AF108105), HAdV-19 (DQ149618, EF121005), HAdV-20 (DQ149619), HAdV-22 (DQ149620, FJ404771), HAdV-23 (DQ149621), HAdV-24 (DQ149622), HAdV-25 (DQ149623), HAdV-26 (DQ140624, EF153474), HAdV-27 (DQ149625), HAdV-28 (DQ149626, FJ824826), HAdV-29 (DQ149627, AB562587), HAdV-30 (DQ149628, AF447393), HAdV-32 (DQ149629), HAdV-D33 (DQ149630), HAdV-36 (DQ149631, GQ384080), HAdV-37 (DQ149632, DQ900900), HAdV-38 (DQ149633), HAdV-39 (DQ149634), HAdV-42 (DQ149635), HAdV-43 (DQ149636), HAdV-44 (DQ149637), HAdV-45 (DQ149638), HAdV-46 (DQ149639, AY875648), HAdV-47 (DQ149640), HAdV-48 (EF153473), HAdV-49 (DQ149641, DQ393829), HAdV-51 (DQ149642), HAdV-53 (FJ169625), HAdV-54 (NC012959), HAdV-56 (HM770721), HAdV-58 (HQ883276), HAdV-59 (JF799911), and HAdV-4 (AY487947) were used as reference strains.