Volume 19, Number 8—August 2013
Dispatch
Duck Liver–associated Outbreak of Campylobacteriosis among Humans, United Kingdom, 2011
Figure 2
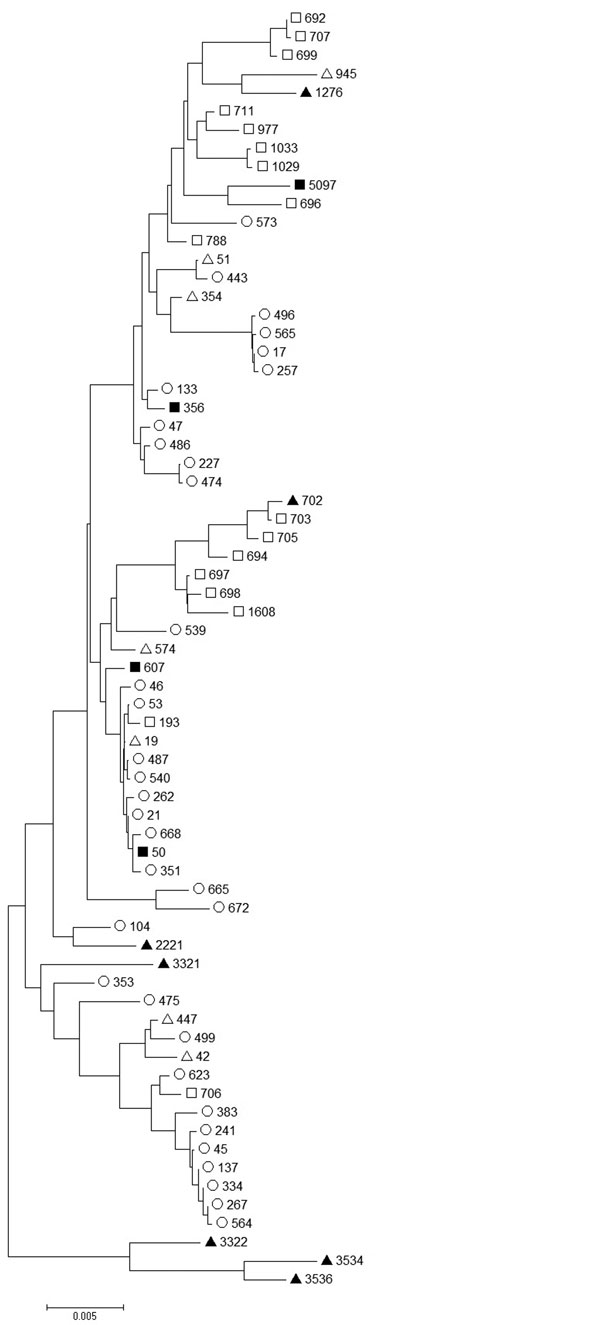
Figure 2. . Comparison of Campylobacter jejuni sequence types (STs) from a duck liver–associated outbreak of campylobacteriosis among humans in the United Kingdom during 2011 (solid squares) with published sequence types of isolates from chicken (hollow circles) (9,10), domesticated duck (hollow triangles) (11), wild duck (solid triangles) (11), and wild geese (hollow squares) (12). ST5097 was isolated from a duck liver sample, ST356 from 3 case-patients, and ST50 and ST607 each from 1 case-patient. Scale bars indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Pebody RG, Ryan MJ, Wall PG. Outbreaks of Campylobacter infection: rare events for a common pathogen. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev. 1997;7:R33–7 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Frost JA, Gillespie IA, O'Brien SJ. Public health implications of Campylobacter outbreaks in England and Wales, 1995–9: epidemiological and microbiological investigations. Epidemiol Infect. 2002;128:111–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Friedman CR, Neimann J, Wegener HC, Tauxe RV. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infection in the United States and other industrialized nations. In: Nachamkin I, Blaser MJ, editors. Campylobacter. Washington (DC): ASM Press; 2000. p. 121–38.
- Little CL, Gormley FJ, Rawal N, Richardson JF. A recipe for disaster: outbreaks of campylobacteriosis associated with poultry liver pâté in England and Wales. Epidemiol Infect. 2010;138:1691–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- O'Leary MC, Harding O, Fisher L, Cowden J. A continuous common-source outbreak of campylobacteriosis associated with changes to the preparation of chicken liver pâté. Epidemiol Infect. 2009;137:383–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Forbes KJ, Gormley FJ, Dallas JF, Labovitiadi O, MacRae M, Owen RJ, Campylobacter immunity and coinfection following a large outbreak in a farming community. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:111–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sheppard SK, Dallas JF, Strachan NJ, Macrae M, McCarthy ND, Wilson DJ, Campylobacter genotyping to determine the source of human infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:1072–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Colles FM, McCarthy ND, Sheppard SK, Layton R, Maiden MC. Comparison of Campylobacter populations isolated from a free-range broiler flock before and after slaughter. Int J Food Microbiol. 2010;137:259–64. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Manning G, Dowson CG, Bagnall MC, Ahmed IH, West M, Newell DG. Multilocus sequence typing for comparison of veterinary and human isolates of Campylobacter jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69:6370–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sheppard SK, Dallas JF, MacRae M, McCarthy ND, Sproston EL, Gormley FJ, Campylobacter genotypes from food animals, environmental sources and clinical disease in Scotland 2005/6. Int J Food Microbiol. 2009;134:96–103. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Colles FM, Ali JS, Sheppard SK, McCarthy ND, Maiden MCJ. Campylobacter populations in wild and domesticated Mallard ducks (Anas platyrhynchos). Environ Microbiol Rep. 2011;3:574–80.
- Colles FM, Dingle KE, Cody AJ, Maiden MC. Comparison of Campylobacter populations in wild geese with those in starlings and free-range poultry on the same farm. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008;74:3583–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Whyte R, Hudson JA, Graham C. Campylobacter in chicken livers and their destruction by pan frying. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2006;43:591–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Khalafalla FA. Campylobacter jejuni in poultry giblets [in German]. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1990;37:31–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: July 19, 2013
Page updated: July 19, 2013
Page reviewed: July 19, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.