Volume 20, Number 4—April 2014
Dispatch
Spread of Virulent Group A Streptococcus Type emm59 from Montana to Wyoming, USA
Figure
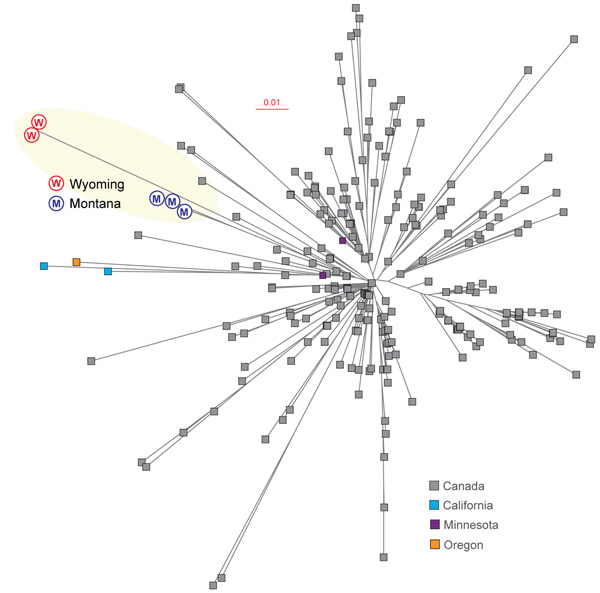
Figure. . Inferred genetic relationships among group A Streptococcus emm59 strains on the basis of 773 concatenated single nucleotide polymorphisms identified by genome sequencing. Strains from Montana (M) and Wyoming (W), USA, are shown in blue and red, respectively. Strains from Canada, and from California, Minnesota, and Oregon, USA, are shown for reference. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
1Current affiliation: Memorial Hospital of Sweetwater County, Rock Springs, Wyoming, USA.
Page created: February 28, 2014
Page updated: February 28, 2014
Page reviewed: February 28, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.