Volume 20, Number 4—April 2014
Letter
Pandemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Maryland, USA, 2012
Figure
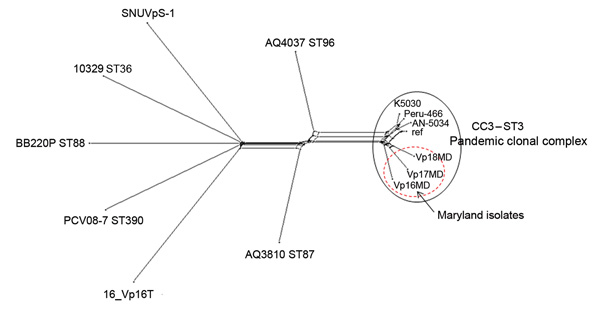
Figure. . Neighbor-Net graph generated with the Bacterial Isolate Genome Sequence Database genome (BIGSdb) comparator tool implemented within the Vibrio parahaemolyticus MLST database (http://pubmlst.org/vparahaemolyticus) (7,8) using 2,613 variable loci. These loci were identified by using as a reference (ref) the V. parahaemolyticus strain RIMD2210633 chromosome I (3,080 genes) and conducting a whole-genome MLST (wgMLST) for V. parahaemolyticus genomes available through GenBank (AN-5034 O4:K68 ST3, Peru-466 ST3, K5030 ST3, 16_VP16T, AQ3810 ST87, AQ4037 ST96, PCV08–7 ST390, BB220P ST88, and SNUVpS-1) and 3 Maryland outbreak strains (Vp16MD, Vp17MD, and Vp18MD). This typing showed that these 3 strains belonged to the pandemic CC3. A similar graph was obtained by using chromosome II of the same strain as reference (data not shown). In brief, the BIGSdb genome comparator tool performs wgMLST, which produces a color-coded wgMLST output (Technical Appendix 2) that facilitates comparison among isolates. This loci output is further categorized into loci that are 1) variable among all isolates, 2) identical among all isolates, 3) missing in all isolates, and 4) incomplete because of being located at the ends of contigs. The variable loci among all isolates are the loci used for assessing relationships and producing a distance matrix based on the number of variable alleles; the strains are resolved into a network by using the NeighborNet algorithm (9). MLST, multilocus sequence typing; CC, clonal complex; ST, sequence type.
References
- González-Escalona N, Cachicas V, Acevedo C, Rioseco ML, Vergara JA, Cabello F, Vibrio parahaemolyticus diarrhea, Chile, 1998 and 2004. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:129–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- González-Escalona N, Martinez-Urtaza J, Romero J, Espejo RT, Jaykus LA, DePaola A. Determination of molecular phylogenetics of Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains by multilocus sequence typing. J Bacteriol. 2008;190:2831–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nair GB, Ramamurthy T, Bhattacharya SK, Dutta B, Takeda Y, Sack DA. Global dissemination of Vibrio parahaemolyticus serotype O3:K6 and its serovariants. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007;20:39–48. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- DePaola A, Kaysner CA, Bowers J, Cook DW. Environmental investigations of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oysters after outbreaks in Washington, Texas, and New York (1997 and 1998). Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000;66:4649–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Abbott SL, Powers C, Kaysner CA, Takeda Y, Ishibashi M, Joseph SW, Emergence of a restricted bioserovar of Vibrio parahaemolyticus as the predominant cause of vibrio-associated gastroenteritis on the West Coast of the United States and Mexico. J Clin Microbiol. 1989;27:2891–3 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jolley KA, Maiden MC. BIGSdb: scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11:595. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jolley KA, Hill DM, Bratcher HB, Harrison OB, Feavers IM, Parkhill J, Resolution of a meningococcal disease outbreak from whole-genome sequence data with rapid Web-based analysis methods. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:3046–53. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jolley KA, Maiden MC. Automated extraction of typing information for bacterial pathogens from whole genome sequence data: Neisseria meningitidis as an exemplar. Euro Surveill. 2013;18:20379 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bryant D, Moulton V. Neighbor-net: an agglomerative method for the construction of phylogenetic networks. Mol Biol Evol. 2004;21:255–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Makino K, Oshima K, Kurokawa K, Yokoyama K, Uda T, Tagomori K, Genome sequence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a pathogenic mechanism distinct from that of V. cholerae. Lancet. 2003;361:743–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar