Volume 20, Number 6—June 2014
Dispatch
Sequential Gastroenteritis Episodes Caused by 2 Norovirus Genotypes
Figure 1
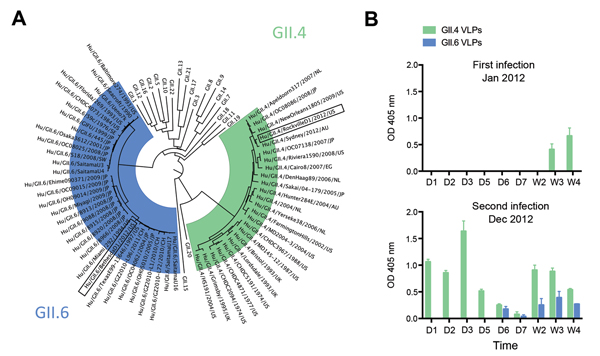
Figure 1. Characterization of norovirus detected in stool samples and levels of local IgA responses for each infectionA) Phylogenetic tree of the major capsid protein (VP1) region from representative norovirus strains from each of the 22 genotypes within strain GIIRepresentative strains from each GII.4 and GII.6 cluster were compared with the strains reported in this article (boxed)For each strain, the name/year/country of isolation are shownB) Levels of IgA in feces collected during the first (G11.4) and (G11.6) second infectionsELISA plates were coated with 1 μg/mL of each virus-like particle (VLP)Fecal samples were collected daily (D) and weekly (W), diluted to 1:500 in phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.4), and tested for the presence of IgA with a polyclonal anti-human IgA conjugateThe experiment was performed twice in duplicate wellsBars represent mean; error bars represent the standard errors of the meanOD, optical density.