Volume 7, Number 5—October 2001
Research
Molecular Identification of Streptomycin Monoresistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis Related to Multidrug-Resistant W Strain
Figure 1
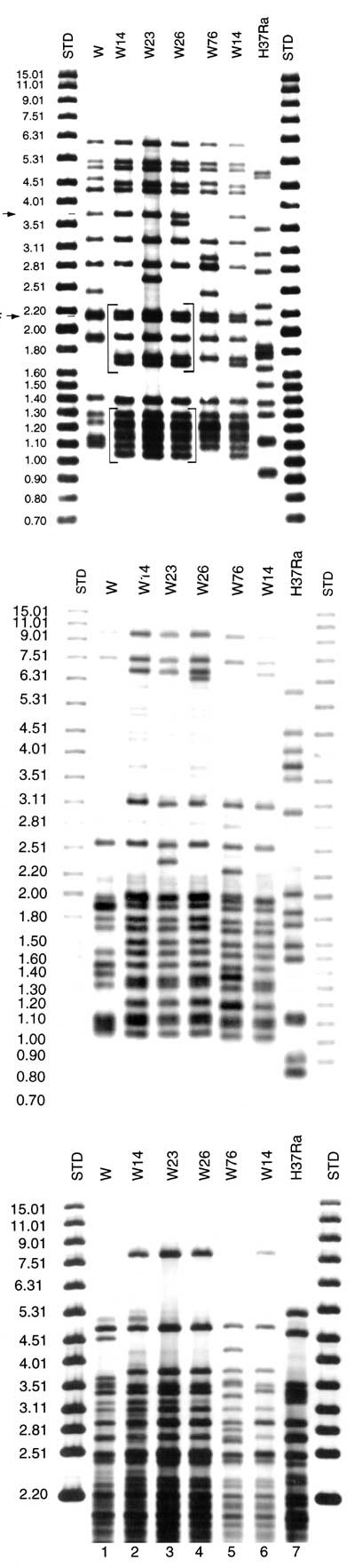
Figure 1. . Southern blot hybridization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates. A) IS6110-3' was used as a hybridization probe. The bracketed pattern motives regions are characteristic of the W14 family. A1 and NTF denote the bands corresponding to the IS6110 insertions in the dnaA-dnaN region and the NTF locus, respectively. Lanes 1 and 9 are standard markers; lane 2: W-MDR from New York City (W index strain); lane 3, 4, 5 and 7: members of the W14 family; lane 6: W76 and lane 8: laboratory control strain H37Ra. B) Southern blot hybridization with IS6110-5' probe. W23 and W26 each have one additional band from W14, when hybridized with either the 3' or 5' IS6110 probe. C) The polymorphic GC-rich repetitive sequence was used as a probe. The W14 group (W14; W23; W26) has a distinctive pattern when compared to all other isolates typed by polymorphic GC-rich repetitive sequence probe.