Volume 14, Number 12—December 2008
Letter
Equine Herpesvirus Type 9 in Giraffe with Encephalitis
Figure
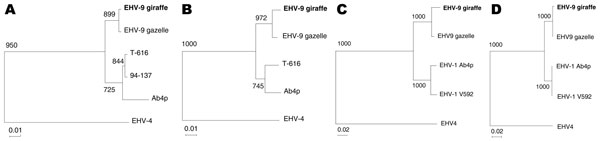
Figure. Phylogenic trees of giraffe herpesvirus and other related viruses. A) Open reading frame (ORF) 30, B) ORF33, C) ORF71, and D) ORF72. EHV-9 giraffe, equine herpesvirus (EHV) type 9 isolated from reticulated giraffe (5) (AB453826); EHV-9 gazelle, EHV-9 isolated from a Thomson’s gazelle in Japan (3) (AP010838); T-616, EHV-1 isolated from a zebra fetus in the United States (EU087295); 94-137, EHV-1 isolated from a Thomson's gazelle in the United States (EU087297); Ab4p, EHV-1 isolated from horses (AY665713); EHV-4, EHV-4 isolated from horses (AF030027). Accession numbers of the sequences are AB439722 for ORF30, AB439723 for ORF33, AB453825 for ORF71, AB453826 for ORF72 of giraffe herpesvirus (DNA Data Bank of Japan, National Institute of Genetics, Japan), and AP010838 for EHV-9 genome sequence (H. Fukushi, unpub.data). Boldface indicates the sequence of EHV-9 derived from the giraffe. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Rebhun WC, Jenkins DH, Riis RC, Dill SG, Dubovi EJ, Torres A. An epizootic of blindness and encephalitis associated with a herpesvirus indistinguishable from equine herpesvirus I in a herd of alpacas and llamas. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1988;192:953–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ibrahim ESM, Kinoh M, Matsumura T, Kennedy M, Allen GP, Yamaguchi T, Genetic relatedness and pathogenicity of equine herpesvirus 1 isolated from onager, zebra and gazelle. Arch Virol. 2007;152:245–55. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fukushi H, Tomita T, Tanaiguchi A, Ochiai Y, Kirisawa R, Matsumura T, Gazelle herpesvirus 1: a new neurotropic herpesvirus immunologically related to equine herpesvirus 1. Virology. 1997;227:34–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Borchers K, Wiik H, Frölich K, Ludwig H, East ML. Antibodies against equine herpesviruses and equine arteritis virus in Burchell’s zebras (Equus burchelli) from the Serengeti ecosystem. J Wildl Dis. 2005;41:80–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hoenerhoff MJ, Janovitz EB, Richman LK, Murphy DA, Butler TC, Kiupel M. Fatal herpesvirus encephalitis in a reticulated giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis reticulata). Vet Pathol. 2006;43:769–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yamada S, Matsumura T, Tsujimura K, Yamaguchi T, Ohya K, Fukushi H. Comparison of the growth kinetics of neuropathogenic and nonneuropathogenic equid herpesvirus type 1 (EHV-1) strains in cultured murine neuronal cells and the relevance of the D/N752 coding change in the DNA polymerase gene (ORF30). J Vet Med Sci. 2008;70:505–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gordon D, Abajian C, Green P. Consed: a graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genome Res. 1998;8:195–202.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Richman LK, Montali RJ, Garber RL, Kennedy MA, Lehnhardt J, Hildebrandt T, Novel endotheliotropic herpesviruses fatal for Asian and African elephants. Science. 1999;283:1171–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Weigler BJ. Biology of B virus in macaque and human hosts: a review. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;14:555–67.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Van Maanen C. Equine herpesvirus 1 and 4 infection: an update. Vet Q. 2002;24:58–78.PubMedGoogle Scholar