Volume 15, Number 8—August 2009
Research
Entomologic and Virologic Investigation of Chikungunya, Singapore
Figure 2
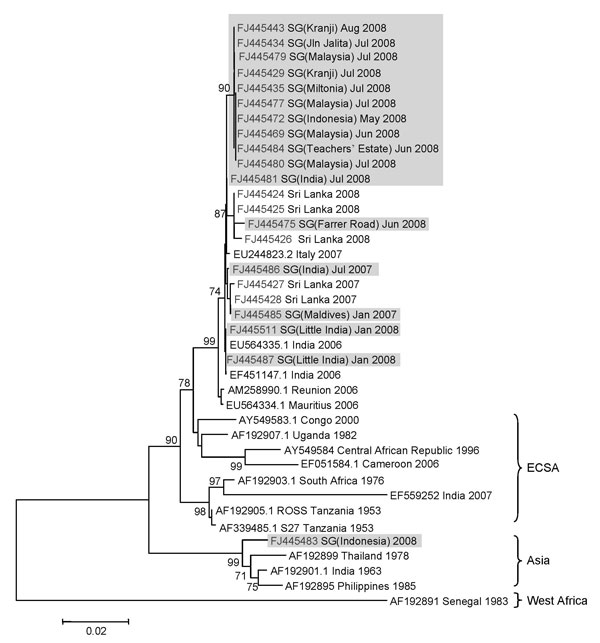
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of the chikungunya virus (CHIKV) envelope 1 (E1) gene. The maximum-likelihood method was used to construct the phylogenetic tree by using 1,002 nucleotides of the sequence of the E1 gene from codons 91 to 424. The tree included 17 isolates detected in Singapore (shaded), 5 Sri Lankan isolates sequenced at the Environmental Health Institute, and 17 global sequences selected to represent all known phylogenetic lineages. In the tree, all sequences are labeled with GenBank accession numbers and country of origin, and are isolated by year/month. In addition, all locally acquired and imported Singapore isolates are labeled with the reported area and country of origin, respectively, within parentheses. Only the bootstrap values >70 are shown on branches. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. ECSA, East, Central and South African genotype; SG, Singapore.