Volume 16, Number 3—March 2010
Dispatch
Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis and 2 Human Deaths, Peru
Figure 2
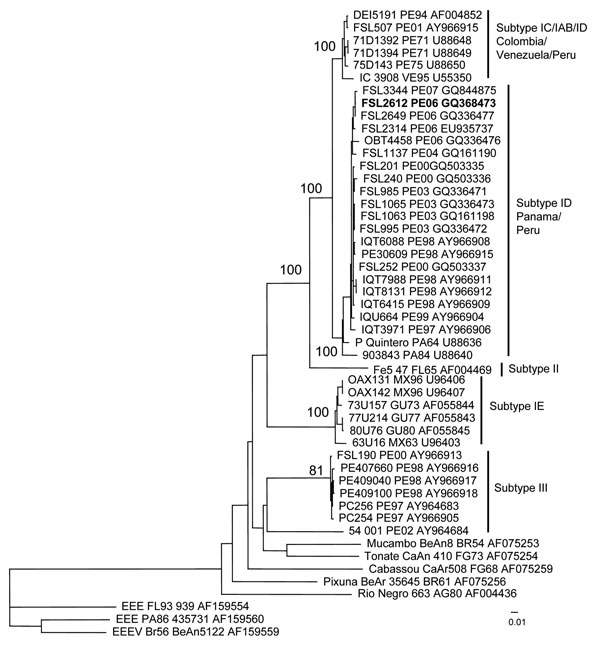
Figure 2. Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV) complex based on partial sequence of the PE2 segment (nucleotide positions ≈8385–9190 of the VEEV genome). The tree was rooted by using an outgroup of 3 major lineages of Eastern equine encephalitis virus (EEEV). The strain isolated from a 7-year-old girl who died from acute VEEV infection in Peru, June 21, 2006, is in boldface. Viruses are labeled by code designation, abbreviated location name, year of isolation (last 2 digits of year only), and GenBank accession numbers of the corresponding sequences. PA, Panama; GU, Guatemala; MX, Mexico; FG, French Guiana; VE, Venezuela; BR, Brazil; AG, Argentina; PE, Peru; FL, Florida. Numbers indicate bootstrap values. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.