Volume 16, Number 7—July 2010
Dispatch
Saffold Cardioviruses of 3 Lineages in Children with Respiratory Tract Infections, Beijing, China
Figure 1
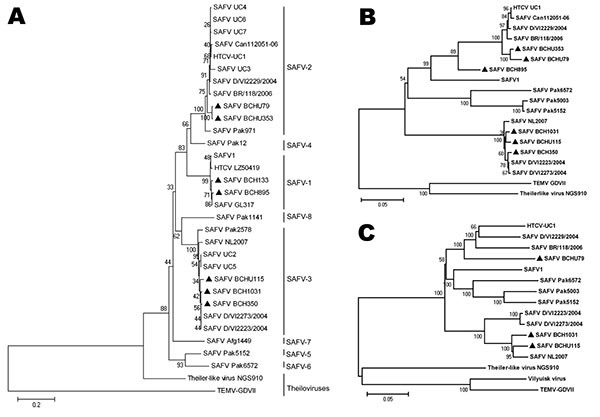
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of Saffold cardiovirus (SAFV) strains obtained in Beijing, China, 2007–2009, based on viral protein (VP) 1 (A), P1 capsid proteins (B), and full-length genomes (C). The trees, with 500 bootstrap replicates, were generated by using the neighbor-joining algorithm in MEGA 4.0 (10). Strains identified in this study are indicated by a specific identification code (BCH or BCHU), followed by the patient number and labeled with dark triangles (BCH133, BCH350, BCH895, BCH1031, BCHU79, BCHU115, and BCHU353). GenBank accession nos. of the complete genome sequences are BCH1031 GU943513, BCHU115 GU943514, and BCHU79 GU943518; of the P1 gene, BCH350 GU943515, BCH895 GU943516, and BCHU353 GU943517; and of the VP1 gene of BCH133, GU126461. SAFV-1 (prototype), UC1-UC7, Can112051-06, D/VI2229/2004, BR/118/2006, D/VI2273/2004, D/VI2223/2004, LZ50419, GL317, Pak12, Pak971, Afg1449, Pak1141, Pak2578, Pak5003, Pak5152, Pak6572, and NL2007, TEMV-GDVII, Theiler-like virus NGS910, and Vilyuisk virus were used as reference sequences (GenBank accession nos. NC009448, NC010810, EU604745-EU604750, AM922293, EU681176-EU681179, FJ586240, FJ464767, FJ463600-FJ463602, FJ463604, FJ463605, FJ463615-FJ463617, FM207487, X56019, AB090161, and EU723237). Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.