Volume 7, Number 6—December 2001
Research
The Changing Epidemiology of Leptospirosis in Israel
Figure 2
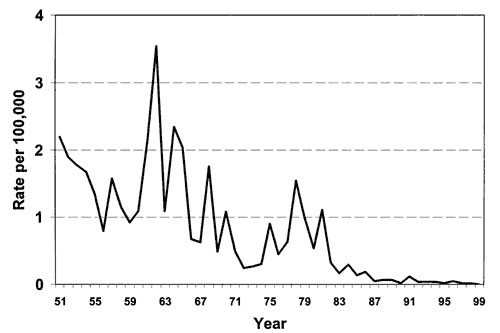
Figure 2. Incidence (rate per 100,000) of leptospirosis in Israel from 1951 to 1999 (adapted from ref. 3, with permission).
References
- Shenberg E, Gerichter B, Lindenbaum I. Leptospirosis in man: Israel 1970-1979. Am J Epidemiol. 1982;115:352–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lindenbaum I, Eylan E, Shenberg E. Leptospirosis in Israel: a report of 14 cases caused by Icterohemorrhagiae serogroup (1968-1982). Isr J Med Sci. 1984;20:123–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Israel Center for Disease Control. Notifiable infectious diseases in Israel, 1951-1995. Tel Hashomer (Israel): The Center; 1996 Sept. Publication no. 201.
- Lindenbaum I, Eylan E. Leptospirosis in Rattus norvegicus and Rattus rattus in Israel. Isr J Med Sci. 1982;18:271–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pate G, FitzSimon N, Mellotte GJ. Leptospirosis in the South-Eastern Health board region of the republic of Ireland: 1990 to 1996. Commun Dis Public Health. 1999;2:217–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Summary of notifiable diseases, United States, 1998. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1999;47:1–93.
- Ciceroni L, Stepan E, Pinto A, Pizzocaro P, Dettori G, Franzin L, Epidemiological trend of human leptospirosis in Italy between 1994-1996. Eur J Epidemiol. 2000;16:79–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Olszyna DP, Jaspars R, Speelman P, van-Elzakker E, Korver H, Hartskeerl RA. Leptospirosis in the Netherlands. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1998;142:1270–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vinetz JM, Glass GE, Flexner CE, Mueller P, Kaslow DC. Sporadic urban leptospirosis. Ann Intern Med. 1996;125:794–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ko AI, Reis MG, Dourado CMR, Johnson WD, Riley LW; Salvador Leptospirosis study group. Urban epidemic of severe leptospirosis in Brazil. Lancet. 1999;354:820–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
1Leptospira serovars tested: Serovars of L. interrogans: Ictero copenhagi Weinberg, Javanica Vcldrat-ATCC 233479, Canicola Hond Utrecht IV-ATCC 2347, Australis-ATCC 23605, Grippothyphosa Moskow V-ATCC 23469, Cynopteri Canazone, Sejroe M-84, Pyrogenes-ATCC 23480, Szwajizak Szwajizak, Ballum Castelloni-ATCC 23580, Mini Sari, Burgas, Hardjo, Ballum Mus, Pomona-ATCC 23478, Tarassovi-ATCC 23481, Bataviae ATCC, Sejreo Bratislava, Rachmat-ATCC 23603, Ictero RGA -ATCC 43642 Serovars of L. biflexa: Patoc, Andamana
Page created: December 09, 2010
Page updated: December 09, 2010
Page reviewed: December 09, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.