Volume 9, Number 11—November 2003
Dispatch
Cowpox with Severe Generalized Eruption, Finland
Figure 2
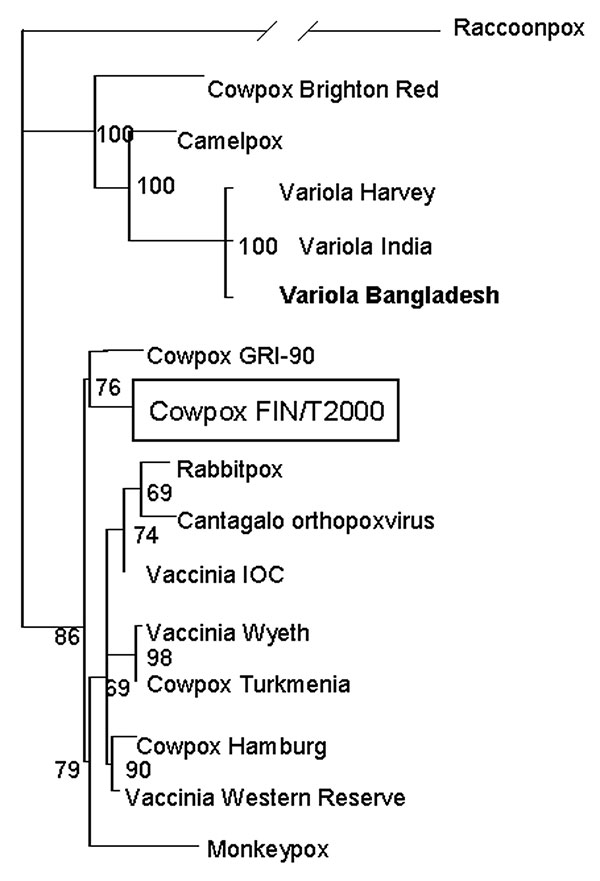
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree of selected orthopoxvirus hemagglutinin genes based on Clustal X alignment and the maximum likelihood method TreePuzzle. Virus sequences used for the analysis were raccoonpox as an outgroup (GenBank accession no. M94169); cowpoxvirus strains Brighton Red (AF482758), FIN/T2000 (AY366477), GRI-90 (Z99047), Hamburg (Z99050), and Turkmenia (Z99048); vaccinia virus strains IOC (AF229248), Western Reserve (M93956), and Wyeth (Z99051); variola virus strains Bangladesh (L22579), Harvey (X65516) and India (X69198); camelpox virus (AF438165); Cantagalo orthopoxvirus (AF229247); monkeypox virus (Z99049); and rabbitpox virus (Z99049).
Page created: March 02, 2011
Page updated: March 02, 2011
Page reviewed: March 02, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.