Volume 9, Number 5—May 2003
Research
Variant Salmonella Genomic Island 1 Antibiotic Resistance Gene Cluster in Salmonella enterica Serovar Albany
Figure 1
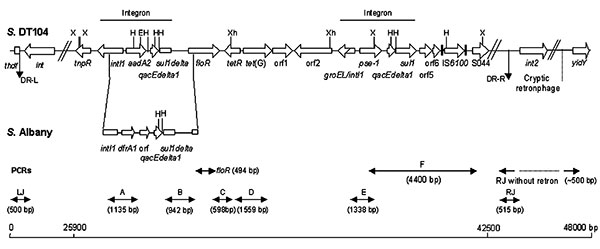
Figure 1. Genetic organization of the antibiotic resistance gene cluster of Salmonella genomic island 1 (SGI1) of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104 and serovar Albany strain 7205.00. DR-L and DR-R are the left and right direct repeats, respectively, bracketing SGI1. Polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) used to assess the genetic organization of the antibiotic resistance genes (PCRs floR, A, B, C, D, E, and F) and the SGI1 junctions to the chromosome (PCRs LJ and RJ for left and right junctions respectively) are indicated. Abbreviations used: S., Salmonella; X, XbaI; H, HindIII; Xh, XhoI; E, EcoRI; orf, open reading frame.
Page created: December 08, 2010
Page updated: December 08, 2010
Page reviewed: December 08, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.