Volume 10, Number 5—May 2004
Research
Genetic Variation of SARS Coronavirus in Beijing Hospital
Figure 2
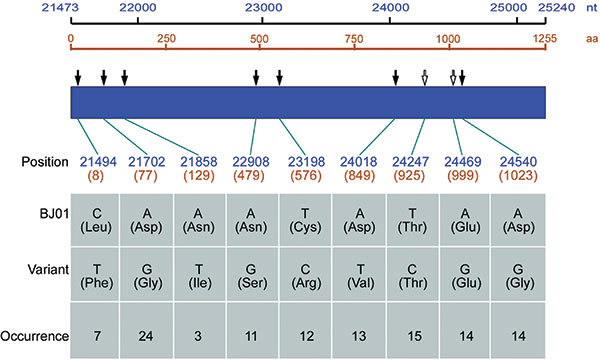
Figure 2. Variants identified from 29 full-length S genes of severe acute respiratory syndrome–associated coronavirus from 20 SARS patients in comparison with BJ01 strain (GenBank accession no. AY278488). The nucleotide positions are numbered according to the sequence of BJ01 strain. Numbers start from the beginning of the genome, but the amino acid numbers start from the S protein. The filled arrows represent nonsynonymous mutations, and the hollow arrows represent synonymous ones. The occurrence indicates the frequency of the variant nucleotide at the given site of the identified 29 entire S genes.
Page created: February 22, 2011
Page updated: February 22, 2011
Page reviewed: February 22, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.