Volume 10, Number 9—September 2004
Research
Genetic Divergence and Dispersal of Yellow Fever Virus, Brazil
Figure 2
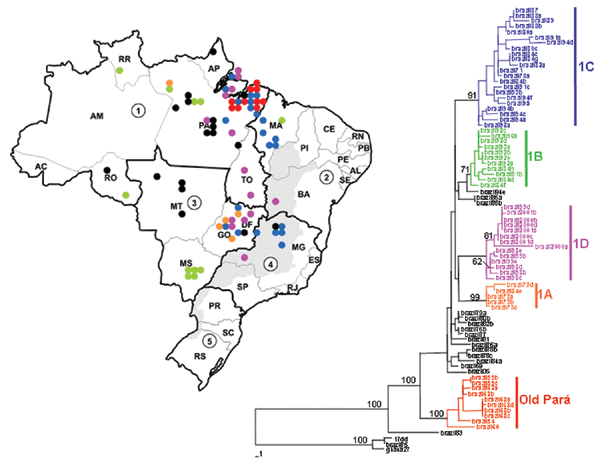
Figure 2. . Brazilian NS5/3´NCR phylogeny (576 nt) based on yellow fever isolates (neighbor-joining tree, Kimura 2-parameter distance correction, midpoint rooted). Geographic origin of isolates is indicated on map. 1: North (AC, Acre; AM, Amazonas; AP, Amapá; PA, Pará; RO, Rondônia; RR, Roraima; TO, Tocantins). 2: Northeast (AL, Alagoas; BA, Bahia; CE, Ceará; MA, Maranhão; PB, Paraiba; PE, Pernambuco; PI, Piaui; RN, Rio Grande do Norte; SE, Sergipe). 3: Central West (DF, Distrito Federal; GO, Goiás; MT,Mato Grosso; MS, Mato Grosso do Sul). 4: Southeast (ES, Espírito Santo; MG, Minas Gerais; RJ, Rio de Janeiro; SP, São Paulo). 5: South (PR, Paraná; SC, Santa Catarina; RS, Rio Grande do Sul). Colors correspond to genetic clade structure. Black dots refer to isolates with unresolved phylogenetic position.