Volume 11, Number 12—December 2005
Research
Antimicrobial-drug Susceptibility of Human and Animal Salmonella Typhimurium, Minnesota, 1997–2003
Figure 3
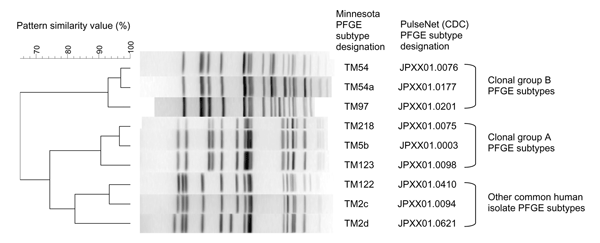
Figure 3. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) patterns of common Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium subtypes observed among clinical isolates from humans and animals in Minnesota. The 3 clonal group B (CGB) PFGE subtypes represent the 3 most common CGB subtypes in animals and humans. The 3 clonal group A (CGA) PFGE subtypes represent the most common CGA subtypes in animals and humans. PulseNet designations are those used in the PulseNet national database of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Page created: February 02, 2012
Page updated: February 02, 2012
Page reviewed: February 02, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.